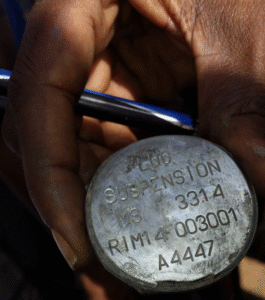Featured Materials
A curated selection of images, terms and collections to help understand modern conflict.

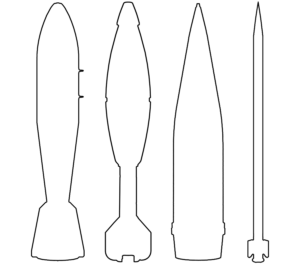
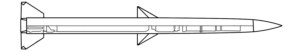
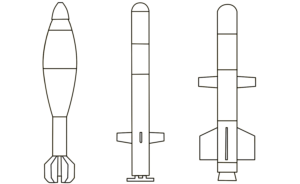
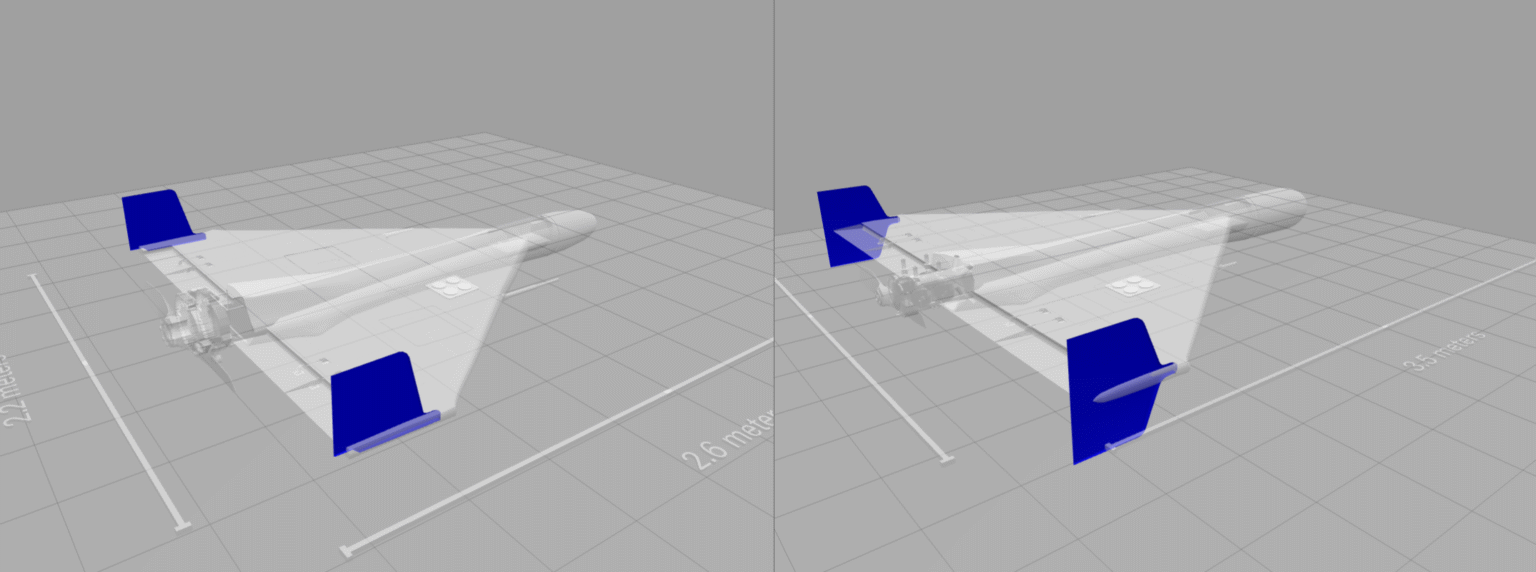
Shahed-131 & -136 UAV
3D models explain the best-known 'kamikaze drones'

Collection
Israel and Gaza 2023 – 2025

Collection
The munitions of the Iran-Israel 12-day war
Шахед‑131 і Шахед‑136 БпЛА
Our visual guide to the Shahed in Ukrainian

GBU-39 bomb
3D model explaining Israel's 'weapon of choice' in Gaza

Research organisation
Images from the Human Rights Watch archives

Collection
The munitions of Trump's Yemen campaign

Collection
Ukraine 2022 – 2026

Follow
Keep up to date with newly added munitions

Contribute
Submit images to the OSMP
1387 results
Analyst Note:
This image shows a WDU-36 series warhead as used in the RGM-/UGM-109 Tomahawk series of cruise missiles. The warhead design suggests this is likely a WDU-36/B from an RGM-/UGM-109E missile. The RGM-/UGM-109E Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (also known as TLAM Block IV) is an improved version of the BGM-109C TLAM-C. In cases where the missile strikes a building but does not function as intended, the dense, comparatively heavy warhead is often projected forwards of the point of impact. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a WDU-36/B warhead as used in the RGM-/UGM-109 Tomahawk series of missiles. The WDU-36/B is the improved, lighter version of the previous WDU-25/B warhead. It is reported that the titanium-cased WDU-36/B weighs around 310 kg and carries a main charge of approximately 120 kg of PBXN-107 high explosives. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a one-way-attack (‘sacrificial’) UAV with the apparent warhead broken off. It is believed to have been attached to the grey mechanism located at the rear of the UAV, likely separating when the UAV was downed. (ARES)
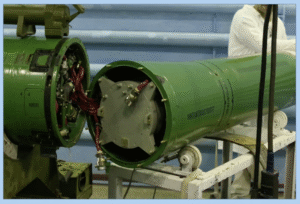
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mk 104 Dual Thrust Rocket Motor (DTRM), the second-stage rocket motor for the SM-2, SM-3 Blk I, and SM-6 missiles. Based on the strakes or fins attached to this Mk 104, it can be determined that it was part of an SM-3 Blk I series missile. (ARES)
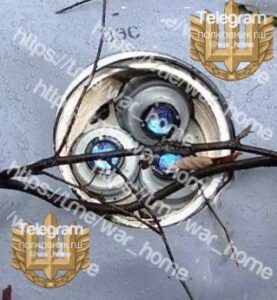
Analyst Note:
This image provides a close-up view of the bottom of the MK 136 Third Stage Rocket Motor section from a RIM-161 Standard Missile 3 (SM-3) Blk I guided missile. The integral warm gas/cold gas attitude control system, including its four venturis, is visible. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the MK 136 Third Stage Rocket Motor of a U.S. RIM-161 Standard Missile 3 (SM-3) Blk I interceptor missile. The SM-3 Blk I variants share the same propulsion sections, but have differences in the kill vehicle section. The SM-3 Blk II variants are substantially different, including new, larger-diameter propulsion sections. SM-3 missiles have a booster, dual-thrust rocket motor, third-stage rocket motor, and an altitude control section in the kill vehicle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image depicts remnants from a M999 (‘Barak Eitan’) 155 mm cluster munition. Reports indicate that the M999 artillery projectile carries nine M99 Dual-Purpose Improved Conventional Munition (DPICM) submunitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Markings on the forward section of this small, air-delivered bomb suggest that the designation is ‘BK-3OF’ (“БК-3ОФ”). The physical features of the munition suggest that it is laser-guided and likely carries a high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) payload. This image shows the only known example, which was allegedly captured by Russian forces in conjunction with a Ukrainian UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a one-way attack (OWA) UAV fitted with a high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead adapted from a PG-7 series recoilless gun projectile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Russian air-delivered cluster bomb is marked with a threatening message directed at the French people: «Français! Changer la politique du président dans le pays, sinon ces bombes vont changer le lieu d'atterrissage!» (“French people! Change the president’s policy in the country, otherwise these bombs will change their landing site!”). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This sheet-metal body component is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR-59518”) which indicates it was produced by GlenDee Corp. of Moorpark, California, which does business as Metalagraphics, Inc. (MGI). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Moog Inc.—headquartered in East Aurora, New York, as marked on this munitions remnant—describes itself as a “worldwide designer, manufacturer, and integrator of precision control components and systems”. Moog supplies actuator and control components to the prime contractor on the Miniature Air-Launched Decoy (MALD) programme, Raytheon. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Hydra-70 rocket fitted with an Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS) guidance kit, converting it into a guided missile. In this case, the missile features an M151 high explosive (HE) warhead fitted with either an M427 or M423 point-detonating (PD) fuze. The rocket motor model cannot be determined from this source alone, but it is most likely to be a MK 66-series motor. The launcher appears to be a LAND-LGR4 model produced by Arnold Defense. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Positive identification of this surface-to-air missile cannot be made based on the imagery in the source. The items highlighted in this image are most likely the remains of either a 9M38- or 9M317-series missile, based on fin construction and their size relative to the individual posing in the foreground. These two missiles are close in design and function, and are predominantly fired from the Buk series of SAM systems. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a ‘120mm TB’ air-delivered bomb that has been adapted from a 120 mm mortar projectile. It is claimed by the manufacturer that this thermobaric munition offers improved fragmentation and blast effects when compared with standard (high explosive) 120 mm mortar projectiles. The “with special FUZE” marking refers to the use of the UT M18 impact fuze. Note that this munition cannot be fired from a mortar, despite the munition body showing features consistent with this use (e.g., gas-check bands). Instead of a standard mortar projectile tailboom which would contain an ignition cartridge and be perforated by flash holes, this munition is fitted with a simplified, plastic tailfin assembly that is designed to stabilise the munition as it falls after being released by a UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9N314M warhead shown here can be used in both 9M38- and 9M317-series missiles. In this particular case, according to the source, it was taken from a 9M38M1 missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Although the source claims that this image shows a Buk-M3 surface-to-air missile system, this imagery is not sufficient to determine whether the remnants highlighted are from a 9M38-or 9M317-series guided missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This guided munition is built around a sacrificial DJI Avata-series UAV that has been fitted with an improvised explosive device (IED). From front to back, it consists of an impact switch made from a syringe, the main charge (yellow/white material in a plastic bag), and a battery that acts as the power source. While crudely made, it is probably still functional. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The physical features of this munition indicate that it is most likely an Iranian 60 mm ‘high explosive, long-range’ (“H.E. L.R.”) mortar projectile fitted with an AZ111A2 impact fuze. However, positive identification cannot be made based on the source imagery. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The munition depicted in this image is a type of aerodynamically optimised artillery projectile, in this case 155 mm in calibre, known as an ‘Extended Range Full-Bore (ERFB)’ design. This example is a cargo projectile fitted with a base-bleed (BB) base unit to further extend its range. This configuration is designated NR269, and reportedly contains 56 M46 dual-purpose (anti-personnel/anti-armour) submunitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this case, the tentative identification of this munition is possible based on an analysis of its silhouette, particularly the distinctive detachable warhead compartment that can be seen hanging from the base of the munition's body. In many cases, such an identification technique would not be possible to apply with confidence. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image represents the first documented instance of a Shahed-series UAV carrying an R-60 air-to-air missile. This appears to add a new capability to the Shahed, enabling it to target enemy aircraft. Arming UAVs to counter interception and engage alternative targets is an emergent trend. Previously, unmanned surface vessels (USVs) employed by the Ukrainian Armed Forces have been observed carrying R-73 air-to-air missiles, for example. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the base of a 155 mm Extended Range Full-Bore (ERFB) projectile, fitted with either a base-bleed (BB) or a base-bleed, rocket-assisted (BB/RA) base unit. Although munitions of this type are capable of carrying submunitions and this image is associated with an incident about which claims of cluster munitions use have been made, there is not enough of the projectile visible in the source images to determine what type of payload was carried by this particular round. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rear section of a Hydra-70 rocket. The Hydra-70 uses the MK 66 series of rocket motors, visible here, but can be fitted with at least 11 different warheads. They can also be fitted with the Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS) ‘bolt-on’ guidance kit, converting an unguided rocket into a guided missile. From the available imagery, it is not clear with which warhead or guidance section this munition may have been fitted. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the venturi and tailfin assembly from a 57 mm S-5 series rocket. The S-5 series of rockets are commonly used around the world in a variety of roles, including air-to-surface and surface-to-surface. Unfortunately, from this image alone the specific model and country of origin cannot be determined. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This munition remnant is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR-05DN8”) which indicates it was produced by Klune Industries. Klune Industries is a sub-contractor on the GMLRS contract. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This munition remnant is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR-62313”) which indicates it was produced by Lockheed Martin. Lockheed Martin is the primary contractor that makes GMLRS missiles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an M49-series 60 mm high explosive (HE) mortar projectile, or a copy thereof. Due to the state of the round the available imagery, the specific model or variant cannot be determined. The fuze is also not clearly visible. Most M49 mortar projectiles use an M525, M717, M935, or similar point-detonating (PD) fuze. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant from an American M30 Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System(GMLRS) missile, which carries M77/M101 submunitions. The yellow diamond markings indicate a payload of explosive submunitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This munition remnant is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR-57413”) which indicates it was produced by the Maine Machine Products Company, a sub-contractor on the GMLRS contract. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows several 107 mm rockets of the Type 63 pattern. Whilst developed by China, munitions of this design are now produced by several countries around the world, including Iran, North Korea, and Sudan. The state-owned Military Industry Corporation (MIC) of Sudan produces a copy of the Type 63 known as the TAKA-01, TAKA-1, or TAKA-107. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Based on the tail-fin assembly design and relative size, the item pictured appears to be a 122 mm rocket. However, it is unclear if this image shows a Russian 9M22-series (‘Grad’) rocket, a Chinese Type 81 rocket, or a similar variant from a different country of origin. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This images appears to show the remnants of a 122 mm rocket. It is unclear what the country of origin is, but it is most likely a 9M22-series or Type 81-series rocket. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
This image shows 122 mm high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectiles manufactured in three different states, L–R: Iran, North Korea, and Russia. Whilst these examples are distinct from one another—particularly in coloration, as well as the presence or absence of paint over the driving band and bourrelet—this is not always the case, and a combination of physical features and markings should be assessed before identification is made. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
This image shows 122 mm high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectiles manufactured in three different states, L–R: Iran, North Korea, and Russia. Whilst these examples are distinct from one another—particularly in coloration, as well as the presence or absence of paint over the driving band and bourrelet—this is not always the case, and a combination of physical features and markings should be assessed before identification is made. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the damaged rocket motor section of a ballistic missile that was fired by the Houthis in Yemen towards Israel and likely intercepted. The Houthis employ ballistic missiles that are supplied by Iran, and given different names. In Houthi service, the Iranian Kheibar Shekan missile is known as the Hatem-2. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows remnants of a Russian Kh-101 air-launched cruise missile. The remnant on the right is the rearmost tail section of the missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the TRDD-50A(M) (ТРДД-50А(M)) turbojet engine, which powers Kh-101 and Kh-59M missiles. Other models of Russian cruise missiles are known to use other variants of the TRDD-50. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The image shows a one-way-attack (OWA) UAV that appears to have crashed, but failed to function. It consists of an FPV chassis, as well as some of the essential components required for flight and the explosive charge (purple container). The initiator and other parts relevant to both flight and the munition’s function are not visible. This appears to be craft-produced ‘sacrificial’ UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This photo shows some of the lithium-ion power banks found within a Gerbera UAV. These are used to power the onboard avionics, control surfaces, communications hardware, camera, and other components. The quantity and type of batteries fitted to the Gerbera will often vary based on the role for which the UAV has been configured—one-way attack (OWA; i.e., a ‘sacrificial’ munition), reconnaissance, signal relay, or decoy—and which specific hardware has been installed to effect this mission. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This photo shows the fuel bladder of a Gerbera UAV, which still contains some fuel. It is likely that a bladder is used—rather than a rigid tank—to save on both weight and cost. Some variants of the Gerbera have been observed to be fitted with a second bladder in the forward section of the fuselage, serving to extend the UAV’s range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The DLE60 two-stroke petrol (gasoline) engine pictured here is the standard engine found on Gerbera UAVs. It is produced by the Chinese company Mile Haoxiang Technology Co., Ltd. and marketed specifically for use in UAVs. Although the Gerbera is manufactured in Russia, the engine and many other key components continue to be supplied from Chinese sources. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Controlled Reception Pattern Antennas (CRPA) unit installed on a Gerbera-series UAV. CRPAs are specialised antenna arrays that help protect GPS receivers from interference, spoofing, and jamming. This particular model, featuring four antennas, was first observed on the Shahed-136 UAV and has since been routinely seen fitted to Gerbera-series UAVs. An alternative array, with six antenna elements, has also been observed, reflecting the varied and ever-evolving state of electronic warfare in Ukraine. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
A Gerbera-series UAV is pictured here being carried by just two Ukrainian soldiers. This highlights the Gerbera’s lightweight design—the airframe is mostly constructed from Styrofoam and wood, which saves on both weight and cost. This particular example does not bear signs of significant damage, suggesting that it either malfunctioned or was brought down by EW and crashed. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an A40 Pro camera, manufactured by the Chinese company Viewpro UAV and design specifically for use in UAVs. The black box to the right of the camera is the control box which manages video output, camera control, and power. The manufacturer claims this model has a 40× optical zoom, AI detection and tracking, and 3-axis gyro-stabilisation. The company further claims that it can customise the onboard AI recognition based on “target characteristics” provided by the client. Numerous Gerberas fitted with this model of camera are known to have been recovered by Ukrainian forces, although it is by no means the only camera model in use. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the back surface of a wireless communications module contained within a downed Gerbera UAV. Although labeled as an HX-50 model designed for fixed locations, Ukrainian military analysis indicates this is an XK-F358 mesh-network module more suitable for use in UAVs. See OSMP1646 for further details. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the front and interior surfaces of a wireless communications module recovered from a downed Gerbera UAV. Although labelled as an HX-50 industrial wireless modem (compatible with WiFi and 5G/4G networks and designed for fixed locations), analysis by Ukrainian military sources indicates that this component is, in fact, an XK-F358 mesh-network module which offers significantly more capabilities. Manufactured and sold by Shenzhen Xingkai Technology Co., Ltd., these modules are designed for, amongst other things, use in robots and unmanned vehicles. Gerbera UAVs have been found operating on a wide variety of frequencies and networks, and this type of module is well-suited to this use. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Pictured is a navigation/GPS module recovered from a downed Gerbera UAV. This particular model is used with the 4-antenna CRPA module seen in OSMP1648. The four RX ports on the bottom are normally directly connected to the CRPA (antenna) module, with other connections made to the UAV’s flight controller and power sources. Some Gerberas have been recovered with CRPA modules bearing a different number of antennas; different navigation modules have been observed on these. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This munition remnant is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR CAGE CODE: 62313”) which indicates it was produced by Lockheed Martin. Lockheed Martin is the primary contractor that makes GMLRS missiles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This remnant shows a munition component marked with the CAGE Code for a sub-contractor who produced part of a larger munition. “64344” is the code for Unique Electronics Inc., a known sub-contractor working on Lockheed Martin’s GMLRS contract. One of the parts they make is the “CABLE ASSEMBLY W459“, as seen in this image. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the three lenses that form the new version of the Kh-101 Digital Scene Matching Area Correlator (DSMAC) system. (The older version only had a single lens.) DSMAC systems take digital images of the ground as the missile passes overhead, and then compare those images to pre-captured images stored in the onboard memory. The DSMAC corrects the flight path as needed based on differences between the two sets of images. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the second warhead present in some variants of the Kh-101 cruise missile. The inclusion of this additional warhead requires a smaller fuel tank in the missile, offering increased explosive weight in exchange for a reduced maximum range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows parts from at least three fin-stabilised tank gun projectiles, including the tail assemblies and several folding fins. These are components that often survive relatively intact following the functioning of such munitions. The specific morphology of the remnants pictured is consistent with Israeli 120 mm tank gun projectiles. Contextual information suggests that the remnants are most likely to be from M339 high explosive ‘multi-purpose’ projectiles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of a control fin from a Paveway III bomb guidance kit that is compatible with 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bombs. In U.S. service, this combination receives designations in the GBU-24 series. Based off this remnant alone, it cannot be determined which model of air-delivered bomb was paired with this particular guidance kit. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows markings on an SUU-30H/B dispenser which comprises part of a CBU-52B/B Cluster Bomb Unit, including a National Stock Number (“NSN 1325 00 477 2053-E800”), design reference (“AF DRAWING NO: 716514-10”), total explosive weight of the submunitions (“CYCLOTOL: 133 LBS:”), lot number (“LOT NO: MA-77G246-002”), and serial number (“SERIAL NO: EE-97391”). This lot number indicates that this CBU-52B/B was manufactured at the Milan Army Ammunition Plant in the U.S. in July 1977. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows part of an SUU-30H/B dispenser (cargo munition) that comprises part of the CBU-52B/B ‘Cluster Bomb Unit’. A CBU-52B/B comprises a SUU-30H/B dispenser that is loaded with 217 BLU-61A/B anti-personnel submunitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows one of two tail fin sections that are attached to an SUU-30H/B air-delivered dispenser (cargo munition). Similar tail fins are used in other variants of the SUU-30 series dispensers. The SUU-30H/B can be used in various ‘Cluster Bomb Units’ including variants of the CBU-52, CBU-58, and CBU-71 munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of an SUU-30H/B air-delivered dispenser (cargo munition), that comprised a CBU-58A/B ‘Cluster Bomb Unit’ (CBU). The CBU-58A/B carries 650 BLU-63A/B anti-personnel submunitions, that have a total explosive weight of 163 lbs (~74 kg) of COMP B explosive; this is reflected in the visible markings. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a GBU-12 series guided bomb being loaded onto a F-35B belonging to Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 211. Two of the control fins have not yet been installed in the Paveway’s guidance control section. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of a control actuator shaft from a Paveway guidance kit control section, found after a strike in Yemen in 2015. Markings giving the CAGE code for Raytheon (“96214”) and the part number (“2870627-2”) are both visible. The complete remnant can be seen in related entry 1559. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the control fin of a GBU-24 (as seen partially marked), the designation for the combination of a Paveway III guidance kit paired with a 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bomb. This remnant is not enough to determine which model of bomb the kit was originally paired with. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a BLU-111 500-pound-class bomb paired with a Paveway II guidance kit, and an MXU-650 series airfoil group, or tail kit. This combination is designated the GBU-12 series in U.S. service. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows remnants of an MXU-series airfoil group, or tail section, that is paired with Paveway-series bomb guidance kits. The remnant on the right is one of two retractor mechanisms that are present inside the MXU-series airfoil group. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a close up view of an actuator assembly from an AGM-114 ‘Hellfire’ series missile. This assembly is what actuates the control fins, and the attachment point for one of the control fins is visible at the bottom right of the image. This assembly belongs to the control section, which is the rearmost section of the missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the bottom of an MS 3314 suspension lug, which is installed on the MK 81 250-pound-class, MK 82 500-pound-class, and MK 83 1,000-pound-class air-delivered bombs. The remnants of the guidance kit in the related entry indicate that, in this case, the lug was fitted to a MK 83 1,000-pound-class bomb. “A4447” is the CAGE code for the manufacturer of the suspension lug, RWM Italia. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows various remnants of an air-delivered bomb and a Paveway guidance kit. The blue pen provides a scale indicator, which is necessary to identify which variant of aerofoil (‘airfoil’) group the tail fins belonged to. In this case, they are most likely from an MXU-650-series airfoil group, which are paired with MK-82 500-pound-class bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the Mado MD550 engine which is used to power the Shahed-136 series one-way attack drone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows some of the markings on a MK 84 2000-pound-class air-delivered bomb, including model designation (“BOMB MK 84 MOD 4”), weight class (“2000 LBS”), part number (“PART NO 30…03 923AS105”), and production lot (“LOT NO GDT 17 …00…”). Many countries produce MK 80-series bombs, so markings such as lot numbers can determine the country of production. “GDT 17” in the lot number indicates that this munition was produced by General Dynamics Ordnance and Tactical Systems, an American company, in 2017. The Israeli Air Force announced they carried out the specific strike associated with this image, which indicates that this specific bomb was transferred to the Israeli Air Force. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of a JDAM tail kit that was paired with a MK 84 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bomb. The CAGE code (“OUVG2”) for Aeroantenna Technology, an American manufacturer of GPS components for guidance systems, is visible on the wiring. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This still taken from a video released by Iranian state media, shows a one-way-attack UAV purportedly manufactured by Israeli forces operating inside Iran. This UAV was found alongside manufacturing equipment, and additional UAV components, strongly suggesting that it was manufactured or assembled inside Iranian borders. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Israeli-made 122 mm rocket motor found following a strike on Amr School in Gaza City. Although it is not possible to be definitive from this image alone, it is likely that this rocket motor was part of an Israeli ‘Bar’ missile, a guided munition designed for precision strikes in urban areas that uses a 122 mm rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the remnants of an unknown Israeli munition that was used in a strike on Nasser hospital. Reporting on these strikes often refers to this munition as a ‘drone’. The turbojet engine, along with possible wing remnants, indicate that this could be a one-way-attack (OWA) UAV or ‘loitering munition’, consistent with reporting. This same model of munition has been used multiple times in strikes in Gaza, as well as Lebanon and Syria. There is no publicly acknowledged Israeli munition that closely fits these remnants. Entries 1384, 1385, 1386, and 1389 capture other incidents in which this munition was used. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Russian spherical submunition of unknown designation. Whilst this specific example was delivered by a cluster munition variant of the Kh-59MK2 missile, this submunition is known to also be delivered by variants of the Kh-69. A similar, but different, spherical submunition is delivered by some variants of the Kh-101. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the remnants of an unknown Israeli munition that was used in a strike that hit the Nasser hospital in Gaza. The turbojet engine, along with possible wing remnants indicate that this could be a one-way attack UAV or ‘loitering munition’, consistent with some reporting on the strikes. This same model of munition has been used in multiple strikes in Gaza, as well as in Lebanon and Syria. There is no publicly disclosed Israeli munition that neatly matches these remnants. OSMP entries 1384, 1385, 1386, and 1389 show other incidents in which this munition appears to have been used. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows part of a Russian Kh-59MK2 missile that is fitted with a cluster munition warhead. Some of the grey spherical submunitions are visible, both inside and outside the warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the guidance control unit from a Paveway- or Lizard-series bomb guidance kit. The guidance control fins are marked “FOR USE ON MK82” indicating that this guidance control unit was paired with a MK 82-series 500-pound-class bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows remnants of two different rocket motors from AGM-114 series Hellfire missiles. While it cannot be determined by these entries alone, images of the damage from the strike associated with this image, gathered by Mwatana, indicate that both of these AGM-114 missiles were the kinetic AGM-114R9X variant. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows one of the actuated fins of a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) tail kit. The manufacturer CAGE code (“76301”) and the part number (“70P862100-1005”) are visible. This CAGE code corresponds to Boeing, the manufacturer of the JDAM guidance kit, while the part number corresponds to a fin of a JDAM kit compatible with MK-84 and BLU-109 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bombs. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the tail actuation section of a SPICE 250 guided bomb. The control fins are normally attached to this section, and the attachment point for one control fin is visible. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a variety of remnants from an Israeli SPICE 250 guided bomb. One of the bomb’s four control fins is visible at the bottom-left of the image. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the outer casing of the “S250 OPTIC” or SPICE 250 guided bomb, with the markings relatively intact. The markings on this remnant show that, while classified as a 250-pound bomb, the actual weight of this SPICE 250 variant is 288 pounds (131 kg) with only 18.5 pounds (8.4 kg) of explosive material. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the top of the booster of an Arrow 3 interceptor missile, where it connects to the kill vehicle. The Arrow 3 was jointly developed by the United States and Israel, and first entered service in 2017. The date of manufacture marking (“DATE OF MFG: 05/2018”) indicates that this booster was produced in the year after the Arrow 3 first entered service. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the booster of an Israeli Arrow 3 interceptor missile. The Arrow 3 is designed to engage ballistic missiles and is capable of exo-atmospheric interceptions. Once the booster is expended, it separates from the ‘kill vehicle’. The kill vehicle has a sustainer motor that propels it towards the incoming ballistic missile, and uses kinetic impact, rather than an explosive warhead, to disable or destroy its target. This is sometimes called the ‘hit-to-kill’ principle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the control section of the Arrow 2 ‘kill vehicle’, including the control fins. The blast-fragmentation warhead is located in the front section of the kill vehicle, forward of the control section, and is absent here due to the functioned state of the munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rocket motor of an AGM-114 "Hellfire" series guided missile found in Jordan during the 12 day conflict between Israel and Iran. This specific Hellfire missile is likely an air-to-air "C-UAS" variant used to intercept one-way attack drones, such as those launched by Iran towards Israel, rather than the more common air-to-surface Hellfire missile variants. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mikholit that was ejected from the weapons pod of an Israeli Hermes 900 drone that was downed in Iran. This Hermes 900 drone had two weapons pod, each capable of carrying 4 Mikholit bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a improvised rocket-assisted munition (IRAM). This particular munition consists of a 107 mm rocket motor with an industrial gas cylinder fitted in place of the standard warhead. The frost present on the cylinder indicates a pressurised gas was released. The yellow–green residue is consistent with a payload of chlorine gas. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows one of the two improvised air-delivered munitions (IADMs) containing a chemical payload used in an attack by the Syrian Arab Air Force on 7 April 2018 in Douma, Syria. This image shows how the IADM comprises a cradle surrounding an industrial gas cylinder. These cradles typically incorporate fins, wheels, and lifting lugs. The fins and the wheels of the cradle can be seen in this image (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a conventional 122 mm high explosive artillery projectile that has been modified to carry a chemical payload. It is one of several used in an attack by the so-called ‘Islamic State’ on the town of Marea, Syria. The black substance on the ground is suggestive of low-purity sulphur mustard, a chemical warfare agent. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an impact crater, as well as remnants of the frame or ‘cradle’ (red box) that was fitted to the gas cylinder. Cradles associated with this type of Syrian Government chemical munition typically feature fins to help orient the cylinder as it falls, and features to assist with loading the cylinders into aircraft for deployment, such as wheels and lifting lugs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an industrial gas cylinder that was reportedly dropped by a helicopter over Kafr Zeita on 1 October 2016. The gas cylinder ruptured on impact with the ground, dispersing its payload of chlorine gas. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a unexploded Iranian submunition pictured in an awareness poster made by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) Home Front Command. The poster warns people to not touch or disturb the submunition. The IDF reported that about 20 of these submunitions were deployed by a single Iranian ballistic missile, spreading over a radius of 8 kilometres. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an unexploded submunition that was deployed by an Iranian medium-range ballistic missile over Israel. Inert variants of these submunitions were previously observed in an Iranian city following a failed missile test. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The source for this entry reports that these remnants were left behind after the missiles were “recycled“. Explosive remnants of war (ERW) are often recycled for the value of their scrap metal, or ‘harvested’ by militant groups for the explosive material. These recycling attempts may result in the ERW exploding, potentially killing or injuring people. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two BLU-108 submunitions. Each BLU-108 contains 4 smaller submunitions, or ‘skeets’. The BLU-108 at the top has deployed all four skeets, while the bottom example has two skeets still attached. The BLU-108 is fitted with a parachute that is deployed after the submunition separates from its dispenser (e.g., the CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon) to slow its descent, as well as a rocket motor that is thereafter fired to increase the munition’s altitude before it deploys the skeets. Each skeet is able to independently seek out targets using an infrared sensor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the largely intact Microturbo TRI-60-30 turbojet engine from a Storm Shadow/SCALP-EG missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Commercial and Government Entity (CAGE) code marked on this data plate (“0S9G9”) is a now-obsolete code assigned to Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), the manufacturer of the Mikholit air-delivered bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the guidance control unit from an Israeli 'Chameleon 3’ bomb guidance kit. This kit appears similar to those in the Israeli Lizard series of guidance kits, which are derived from the American-designed Paveway kit series. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This is the data plate fitted to an Israeli Air Force bomb guidance kit. It reads “3 זִקִית” (‘Zikit 3’, or ‘Chameleon 3’ in English). As of May 2025, there is no public information available about this model of bomb guidance kit, but it appears to be a derivative or variant of the Israeli Lizard series, which are derived from the American Paveway bomb guidance kit. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the damaged aerofoil group, or ‘tail kit’, found with a Chameleon 3 bomb guidance kit. The exact model of aerofoil group is unknown, but in US service similar component groups are given a designation in the ‘MXU-xxx’ range, and are interchangeable with different variants of the Paveway bomb guidance kit (within bomb weight classes). (ARES).
Analyst Note:
Although Human Rights Watch reported that they found manufacturing markings on a guidance fin assembly indicating that this MXU-series aerofoil group was paired with a Paveway III guidance kit, this cannot be determined by this wing remnant from the aerofoil group alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows fragments of a BLU-109C/B 2,000-pound penetrator bomb. The remnant with visible threads is part of the aft closure ring attached to the base of the bomb. This features nine vent holes as an ‘insensitive munition’ (IM) safety feature. Three of the threaded vent holes are visible on this fragment. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the tail actuator subsystem of a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) bomb guidance kit. The size of this JDAM kit indicates that it is one of the kits compatible with 2,000-pound-class bombs, either the MK-84 or BLU-109. (ARES)
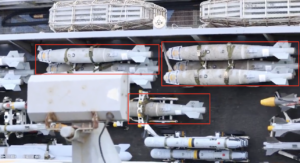
Analyst Note:
This image shows a variety of small air-delivered munitions that have been developed specifically for deployment via UAV. Some of these appear to be original designs, whilst others have been made by modifying existing munitions. This entry reflects those munitions outlined with the red box, but all of the munitions are generally of similar in size and format, and all have tailfin assemblies intended to orient the munition as it falls, just like more traditional air-delivered bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The munition in this image has been integrated into a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) small UAV. This UAV (‘drone’) adds powered and guided delivery and converts the munition into a guided missile—regardless of the original, intended delivery method. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows three sets of three PTM-1 series scatterable anti-vehicle mines taped together. While these mines have likely been repurposed from their original delivery munition to be delivered via UAV, this cannot be confirmed based off this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows four PFM-1 series anti-personnel landmines retained by a release mechanism to enable deployment via UAV. Ordinarily, PFM-1 series and other ‘scatterable mines’ are deployed via carrier munitions or dedicated mine-dispensing devices. In Ukraine and other conflicts, these mines have often been removed from their original carrier munitions in order that they may be delivered via UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an AR731-4000 Wankel-type engine produced by UAV Engines Ltd. of the United Kingdom, used in an Israeli Harop munition. Variants of the Harop used in the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War featured a similar Wankel engine, but were marked to indicate a different manufacturer and model name: “MBT ENGINE” and “H2251-5100-503”, respectively. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the remnants of a SkyStriker one-way attack UAV, manufactured by Elbit Systems of Israel. The SkyStriker can be fitted with various warhead options, including dual-purpose warheads weighing 5 or 10 kilograms. While it appears that a reconstruction was attempted with the remnants, the placement of the various components does not accurately represent an intact SkyStriker. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The JROF and JROF-K are Czech derivatives of the Soviet 122 mm ‘Grad’ series of surface-to-surface rockets. The JROF-K is the shorter, reduced-range variant, broadly analogous to the Soviet 9M22M. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the BSU-60 A/B tail fin. This this model of tail fin is used exclusively with AGM-88 series missiles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the nosecone from an Israeli SPICE 250 air-delivered bomb. Whilst generally similar in appearance to the nosecone of the GBU-39, the SPICE 250 nosecone is longer and narrower. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the flare from a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system's ‘Talon’ kinetic interceptor missile. The flare is located at the aft end of the missile's booster engine. The ‘petals’ of the flare are initially flush, and are actuated into the deployed position, seen here, as part of the missile‘s functioning. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a fragment of the “inner petal assembly” of a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system’s ‘Talon’ interceptor missile. The part number for the assembly (“23917ASSY1A62803-101 REV.E / E”), Commercial and Government Entity (CAGE) code (“07554”), manufacturer abbreviation (“CTL”), and serial number (“S/N DDLKD”) are visible. This CAGE code and manufacturer abbreviation are associated with CTL Aerospace Inc, a subcontractor for Lockheed Martin, the manufacturer of the THAAD system. It is not uncommon for complex munitions to be made by several different manufacturers, and thus multiple CAGE codes may be present as a result of the various subcontractors. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows three different warheads developed by Russia for the Shahed-136/Geran-2 one-way attack (OWA) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), each of which differ from the original warhead designed by Iran for the Shahed-136. Left: A thermobaric explosive warhead; Middle: TBBCh-50M, a thermobaric explosive warhead; Right: OFZBCh-50, a high explosive warhead with an incendiary effect. Each of these warheads is also fitted with a fragmentation liner to increase the fragmentation effect generated when the warhead detonates. Some of the fragmentation liners may contain zirconium, a metal which is ignited when the warhead detonates, providing an additional incendiary effect. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mikholit glide bomb, with its warhead removed (green cylinder on the left side of the box). The fins that spring outward when deploye have been taped down. This Mikholit was reportedly recovered by the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) from Hamas, who had captured the bomb after it failed to function when originally deployed by the IDF. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two Mikholit air-delivered bombs (‘glide bombs’), and four Mikholit warheads. There are at least two different variants of warheads available for the Mikholit glide bomb. The green cylinder on the left is a blast (high explosive) warhead, whilst the other three warheads are shaped charge warheads which incorporate additional fragmentation. Blast warheads of this type have also been seen with red markings, while the shaped charge warheads have been seen with yellow markings. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows various remnants from GBU-39 air-delivered bombs, including two fuze wells. Each GBU-39 has only a single fuze well, indicating that this picture shows the remnants of at least two different GBU-39 bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image and the related entries show fragments of an AGM-84 Standoff Land Attack Missile-Expanded Response (SLAM-ER) series missile. AGM-84 SLAM-ER missiles are AGM-84E Standoff Land Attack Missiles (SLAM) that incorporate certain upgrades, including wings to increase the missile's range. The AGM-84 series include the anti-ship ‘Harpoon’ variants, from which the SLAM and SLAM-ER series are derived. As a result, many remnants will be similar or identical between variants. The wing remnant here is diagnostic, however. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rear fin section that is attached to a M-302/Khaibar-1/Fadi series rockets to add guidance capabilities. This rear fin section is installed, along with a forward control section between the warhead and the rocket motor. The guided munition, now classified as a missile, is referred to as a Nasr-1/Nasr-2. A similar, but larger, rear fin section is fitted to Zelzal rockets to convert them to guided munitions. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows a MXU-735 solid nose plug that can be installed in the nose fuze well of a MK 80-series aerial bomb in place of a fuze. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows several GBU-53/B bombs photographed from above while on a munitions transport cart. GBU-53/B bombs are transported and loaded onto the aircraft with the wing assembly on the bottom. When the GBU-53/B is released from the aircraft, the bomb rotates, with the wing assembly side orienting as the top as the bomb glides to its target. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a fragment of a RGM/UGM-109 Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) series missile's WDU-36/B warhead. The WDU-36/B warhead is a penetrator warhead for the TLAM, and is one of several available warhead options for TLAM series missiles. The complete "WDU" designation isn't visible, but the part number (3123AS921) is associated with the WDU-36/B. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a strake from a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) guidance kit (KMU-557/558) as fitted to 2,000-pound BLU-109-series penetrator bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rocket motor of a Kheibar Shekan or Fattah-1 medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM). The Fattah-1 was publicly unveiled by Iran in June 2023, with very few images surfacing since that time. Due to the lack of available reference material, differentially identifying the Kheibar Shekan and Fattah-1 is difficult. The missile components displayed at unveilings and public displays are also often different from those used in production models. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows the copper cone of the shaped charge located at the front of the warhead fitted to a Shahed-131. The Ukrainian armed forces have recorded that the cone measures 111 mm in diameter and 162 mm in depth. The warhead is lined with cubic pre-formed fragments of 7 mm in diameter. The explosive content of the warhead is estimated to be between 10 and 15 kg. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two MAM-L guided air-delivered bombs affixed to the wing of a Bayraktar TB2 drone. The MAM-L and TB2 are both produced in Türkiye by Roketsan and Baykar respectively. The MAM-L can have one of three different warheads: blast fragmentation, anti-tank, or thermobaric. The warhead section of each MAM-L in this image has “YIPE/BF” visible. ‘YIPE’ is the abbreviation of the warhead type in Turkish: Yüksek Infilaklı Parçacık Etkili (‘high explosive fragmentation’, in English). The ‘BF’ also indicates that these MAM-L munitions are of the blast-fragmentation variant. The warhead of a MAM-L cannot be determined from an external assessment without viewing markings such as these (or a clear view of the data plate, which can be seen on the aft portion of the MAM-L). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows several remnants of a MAM-L bomb that are typically found after functioning. The actuated fins, as well as the fixed fins, are visible, along with various components of the control section that actuate the fins. The actuated fins attach to the control section, at the rear of the bomb, while the fixed fins attach to the middle of the bomb body. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a fragment of an Israeli 120 mm tank gun projectile, with its distinctive obturating band configuration. The additional remnants shown in the related OSMP entry permit distinguishing this projectile from other potential Israeli models, identifying it as the M339 tank gun projectile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an American F/A-18 fighter aircraft armed with two AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) air-delivered bombs taking off to conduct strikes against Houthi forces in Yemen. The F/A-18 likely has two more AGM-154-series munitions carried on the opposite side of the aircraft, for a total of four bombs. The JSOW has multiple variants which are fitted with different warheads, including a submunition payload (AGM-154A and AGM-154B models), BLU-111 500-pound bomb (AGM-154A-1), and a Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage penetrator warhead (AGM-154C or AGM-154C-1). All variants are externally identical without markings, with the exception that the AGM-154C and C-1 have a small reflective window on the bottom of the nose for the terminal infrared (IR) seeker. The munitions in the image are most likely AGM-154A-1 or AGM-154C-series bombs, due to the lack of reported submunitions following the strikes. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an unexploded WDU-45/B, the second stage or penetrator warhead (also called a ‘follow-through’ warhead), of the Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead system used in the AGM-154C variant of the Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) air-delivered bomb. The first stage is a shaped-charge warhead designed help the second stage penetrate hardened targets before detonating. The Shadow/SCALP-EG missile also uses a multi-stage BROACH system, but with larger warheads. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an RGM-109-series Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) being launched from the USS Curtis Wilbur (DDG 54), an Arleigh Burke-class guided missile destroyer. The RGM-/UGM-109 TLAM series are surface-to-surface cruise missiles fired from various platforms. The ‘R’ and ‘U’ in RGM and UGM, respectively, denote the intended launch platform, with ‘R’ denoting surface platforms, such as ships, and ‘U’ denoting subsurface platforms, such as submarines. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a relatively intact Shahed-131 one-way-attack (OWA) UAV with various components highlighted, including the GPS antenna array (light blue), fuselage (light purple), engine (yellow), wing stabiliser (orange), and nose cone (cyan, inside the red box). The nose cone attaches to the front of the fuselage and covers the warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the aft motor section, which includes the venturi nozzle, of a North Korean KN-23/KN-24/Hwasong-11 series missile. The KN-23/KN-24/Hwasong-11 has a generally similar appearance to the Russian 9M7 ‘Iskander’ series of ballistic missiles, but has differences in performance and in some aspects of the construction. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Iranian M344 106 mm recoilless gun projectile. The M344 is a high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) munition, containing a shaped charge that is designed to penetrate armour. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
These images show a damaged Serat-01 engine which powers the Shahed-131 drone after its rocket-assisted launch. The Serat-01 is a copy of the MDR 208 engine, and is noticeably smaller than the MD550 which powers the larger Shahed-136. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the BSF-50, one of several warheads developed by Russia for the Shahed-136/Geran-2 to replace the original Shahed-136 warhead designed by Iran. The BSF-50 is a high explosive warhead with a fragmentation effect. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the fuzewell in the base of the warhead of a GBU-39 air-delivered bomb. The innermost cylinder is the electronic fuze; this is held in place by the closure ring. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Depicted here is the MD-550 motor of a Shahed-136/Geran-2. This image was presented by Ukrainian President Zelenskyy as a fragment of the drone that reportedly hit the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant’s New Safe Confinement shelter. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Two R-77 air-to-air missiles (NATO reporting name: AA-12 Adder) are carried in this photograph by a Russian Aerospace Forces Sukhoi Su-35 fighter aircraft. Key markings, including the aircraft’s bort number (a coloured numeral that acts as a unit or base identifier), have been digitally obscured. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the functioned rocket motor of an Israeli Carpet rocket. The Carpet uses a fuel-air explosive (FAE) warhead which is designed to function mines and improvised explosive devices (IEDs), clearing a target area for the advance of friendly forces. These rockets are fired from the Carpet rocket launcher, which is loaded with up to 20 rockets and can be fitted to a variety of vehicles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Armement Air-Sol Modulaire (AASM; ‘Modular Air-to-Ground Armament’) family of French bolt-on guidance kits are fitted to air-delivered bombs of various sizes in a similar fashion to American JDAM kits. In some marketing materials, the acronym HAMMER is used, standing for ‘Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range’. This refers, in part, to the rocket boosters fitted to munitions in the family to extend their effective range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this photo, a Ukrainian Sukhoi Su-25 ground-attack aircraft from the 299th Tactical Aviation Brigade, with the bort number ‘Blue 28’, is seen carrying an AASM-250 guided air-delivered bomb under its left wing. Available imagery shows that the AASM-250 has also been fitted to Mikoyan MiG-29 fighter aircraft, and can likely be carried by the Sukhoi Su-27 as well. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rear portions of two different two different Spike Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) missiles, which each include the control section and part of the rocket motor.
The Spike NLOS has been in service with Israel since 1987, and is currently in its sixth generation, or iteration, which comprises an unknown number of variants. At least three different warhead configurations are reported: high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG), high explosive anti-tank (HEAT), and a ‘multipurpose’ or anti-structure variant with a penetrating blast and fragmentation warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a MK 84 2,000-pound bomb that has had its fuze and baseplate removed in order to access the explosive filler. The fuze, fuze retaining ring, and baseplate can be seen on the white sheet.
The explosive material used to fill the bomb has been removed, possibly to be repurposed in improvised explosive devices or craft-produced munitions. Unexploded ordnance is often ‘harvested’ for these purposes. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Israeli Air Force F-16 carrying four Rampage air-to-ground missiles. The Rampage is a 580 kg (1,278 lb) missile with GPS and INS guidance. It carries a multi-purpose warhead that is designed for engaging a range of targets in the open as well as offering some degree of penetration. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the pneumatic accumulator, or ‘accumulator bottle’, of the AGM-114R9X missile. The accumulator bottle stores gas that is used to actuate the fins, adjusting the trajectory of the missile in flight. All AGM-114 Hellfire-series missiles have an accumulator bottle. The accumulator bottle is a fragment that often survives intact, even in Hellfire missile variants that carry an explosive payload. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows various munitions remnants, including a fuzewell and two nosecone fragments from GBU-39 Small Diameter Bombs. The presence of two different nosecones indicates that these remnants are from at least two distinct munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Contextual images of the damage caused by this munition indicate the remnant pictured is from the AGM-114R9X variant of the Hellfire missile, a kinetic munition which does not carry an explosive warhead. This remnant cannot be differentiated from either other AGM-114 or the AGM-179 JAGM variants based off this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a 9M22S rocket with some of its unfunctioned payload of 180 ML-5 incendiary elements. Each ML-5 is a hexagonal prism formed from a hollow shell of magnesium that is filled with an incendiary composition. These elements are ignited by the ejection charge of the rocket’s warhead upon functioning. Two fuzes are also visible at the bottom of the image, immediately above and below the ruler. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This F-16I fighter aircraft from the Israeli Air Force is carrying a CATM-120 inert missile simulant (indicated). These devices are used for training purposes, being designed to replicate the weight and centre of gravity of a live munition. They lack any means of propulsion and are not released from the aircraft. The CATM-120 can be differentiated from the AIM-120 missile series by the presence of only blue bands on the missile, denoting both an inert rocket motor and an inert payload. A ‘live’ AIM-120 will have two brown bands on the rear section of the missile (the rocket motor), and a yellow band on the forward, or warhead, section. An AIM-120 with an inert warhead, but a live rocket motor, will have a blue band on the warhead and two brown bands on the rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a wing fragment from a SPICE-1000 bomb guidance kit. While there are no remnants of the bomb body visible, it can be determined that a MK 83-series 1,000-pound bomb or similar was used, as MK-83 series bombs are paired with the SPICE-1000 bomb guidance kit to form a complete munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a fragment of the wing assembly of a Paveway bomb guidance kit. The data plate, though damaged, provides additional information about the munition. A partial Commercial and Government Entity code (CAGE; “ …14”), manufacturing part number (MFG SKU; “872127-1”), National Stock Number (NSN; “...5-01-141-5890”), serial number (Serial NO; 15-005326), and date of manufacture (“…MFR. 10/15”) are visible. This data can be used to look-up the component and determine that this specific fragment is from a Paveway II guidance kit intended for use with a MK 82-series 500-pound-class air-delivered bomb. This bomb and guidance kit combination is referred to as the GBU-12. The CAGE code, although partial, is enough to determine that this specific kit was produced by Raytheon, rather than the other known manufacturer of the Paveway kits, Lockheed Martin. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a fragment of the wing assembly of a Paveway kit, compatible with a MK 82 500-pound-class air-delivered bomb. (“..R USE ON MK82”). The National Stock Number (NSN; “1325-01-5453531”) indicates that this is a Paveway IV bomb guidance kit. There are variants of Paveway guidance kits compatible with all MK 80-series bombs, as well as other bombs such as the 5,000-pound-class BLU-113 penetrator. Paveway bomb guidance kits use laser guidance, and are more precise than JDAM guidance kits. Some variants of the Paveway kit, such as the ‘Enhanced’ series feature GPS and INS guidance in addition to laser guidance. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows part of the SUU-66 dispenser (sometimes called a ‘shell’) that forms part of a CBU-105 D/B cluster bomb unit. In U.S. service, a ‘cluster bomb unit’ designation includes both the dispenser or shell, as well as the payload.
The CBU-105 series of cluster munitions consists of CBU-97-series munitions that are modified with a WCMD (Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser) guidance kit. Both CBU-97 and CBU-105 series munitions are made-up of an SUU-66 dispenser filled with 10 BLU-108 submunitions. Each BLU-108 submunition contains 4 ‘skeet’ warheads that are ejected mid-air and independently seek out targets using an infrared sensor. A single skeet weighs 7.5 lb (3.4 kg) and contains a copper explosively formed penetrator (EFP) for armour penetration that is surrounded by a fragmentation ring offering some anti-personnel effect. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows three North Korean 120 mm high explosive (HE) mortar projectiles. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows a North Korean 120 mm high explosive (HE) mortar projectile next to an Iranian 120 mm HE mortar projectile. Despite both being the same calibre, the overall shapes and dimensions of the two projectiles are noticeably different. Factors such as payload weight and range can be affected significantly by projectile shape. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The ZAB-250-200 (ЗАБ-250-200) unguided air-delivered bomb is loaded with 48 kg of a napalm-like thickened incendiary mixture, 8 kg of cotton scraps soaked in kerosene (paraffin), and 4 kg of pyrotechnic composition to aid with ignition. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
This image shows one of several possible warhead variants that can be carried by the Shahed-136/Geran-2 one-way attack (OWA) UAV. The Shahed-136/Geran-2 (and the smaller Shahed-131/Geran-1) has been documented carrying shaped-charge warheads, penetrator warheads, and multi-function warheads. Due to the various warheads that can be carried by a Shahed/Geran drone, the functional use cannot be determined without the warhead being visible. In this case, the munition was fitted with a TBBCh-50M warhead that contains a thermobaric explosive composition with an additional fragmentation effect. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Shahed-131/Geran-1 and Shahed-136/Geran-2 one-way-attack (OWA) UAVs can be fitted with on of a variety of warheads with different functional uses. The specific type carried by each UAV cannot be determined unless the munition has been damaged in such a way as to reveal the warhead, such as in this case. This image shows the cone of the shaped charge, indicating that this Shahed-1/Geran-1 carries a warhead with a penetrating or anti-armour effect. This warhead has been documented with 18 additional liners for enhanced anti-armour effect, and in some cases has been fitted with fragmentation liners for an enhanced anti-personnel effect. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Whilst there are no visible markings explicitly identifying the model of the 122 mm rockets in this image, they are sitting atop a box marked “R-122” and exhibit physical features consistent with North Korean R-122 rockets. It should be noted that rockets marked with the generic “R-122” model name have been observed in both ‘long’ and ‘short’ overall lengths and painted in different colours. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Whilst relatively little is known about Burmese air-delivered bombs from publicly available sources, researchers (including those at ARES and Myanmar Witness) have been collecting evidence based on munitions’ physical features and markings. Combined with information from confidential sources, this has allowed for the tentative identification of several models. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This F-16I fighter aircraft from 107 Squadron Israeli Air Force is carrying a CATM-120 inert missile simulant (indicated). These devices are used for training purposes, being designed to replicate the weight and centre of gravity of a live munition. They lack any means of propulsion and are not released from the aircraft. The CATM-120 can be differentiated from the AIM-120 missile series by the presence of only blue bands on the missile, denoting both an inert rocket motor and an inert payload. A ‘live’ AIM-120 will have two brown bands on the rear section of the missile (the rocket motor), and a yellow band on the forward, or warhead, section. An AIM-120 with an inert warhead, but a live rocket motor, will have a blue band on the warhead and two brown bands on the rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M712 ‘Copperhead’ is a laser-guided 155 mm artillery gun projectile carrying a high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead designed to engage armoured vehicles. The Copperhead was developed in the United States in the 1970s, and saw limited use during Operation Desert Storm. The M712 is is pictured here inside its shipping container, and the slots for the enclosed, deployable (‘pop-out’) wings and fins are visible. The M712 has two operational modes: a ballistic mode that follows a gun’s ballistic trajectory like a traditional artillery projectile, and a glide mode, which follows a longer and flatter trajectory. The preferred mode is set by the artillery crew before firing. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
As with several other images in the OSMP database, the text on this image was added by a social media user prior to its inclusion herein. Rather than a “rocket” as described in the annotation, this image actually shows an air-delivered bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The two North Korean 120 mm high explosive (HE) mortar projectiles in this image are each fitted with five cloth bags affixed above the tailfins. These are incremental propellant charges (sometimes known as augmenting, auxiliary, or supplemental charges), the number of which can be varied along with a mortar’s elevation to adjust the trajectory and range of the munition when fired. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two Iranian 130 mm high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectiles. Calibre (“130MM”) and functional type (“HE - TNT”) markings are visible on the right-hand example, whilst a lot marking (“LOT:10/202[…]”) is partially obscured. The “TNT” marking indicates that this munition uses a trinitrotoluene composition as its explosive fill. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This 9M27K-series surface-to-surface cargo rocket is loaded with either 9N210 or 9N235 high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) submunitions. These models are nearly identical in construction, differing primarily in the nature of the pre-formed fragments they carry. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Iranian 122 mm high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectile. Like several other munitions, it is described in Iranian sources—and, in this case, on the munition itself—only by reference to the weapon with which it is most often associated: the Soviet-designed 122 mm D-30 howitzer (often rendered ‘D30’, without the hyphen, in Iranian service). This munition is also marked to indicate it was produced in 2023. Interpreting munitions markings in this way, especially where they indicate recent manufacture, may provide evidence of ongoing supply during a conflict. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Stunner surface-to-air missile fired by the David’s Sling air defence system is a two-stage interceptor, meaning that the munition contains two separate rocket motors for launch and propulsion. The first stage, or launch motor, detaches from the munition after a short time, before the second stage, or flight motor, ignites. The second stage motor, visible here, was found relatively intact. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The munition indicated in this image as a 152 mm high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectile manufactured in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows part of the warhead section of an MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) series tactical ballistic missile. This is the top of the warhead section, where it connects to the guidance section. A data plate is visible, giving information about the manufacturer (“Lockheed Martin Vought Systems”) and identifying this specific part (“WARHEAD, GUIDED MISSILE. HIGH EXPLOSIVE”. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an SUU-30H/B, an air-delivered dispenser which can be configured to carry different submunition payloads. These can include 217 BLU-61 A/B, 650 BLU-63/B, or 650 BLU-86/B or BLU-86 A/B. The munition can also carry inert payloads. The specific combination of payload and dispenser determines the ‘Cluster Bomb Unit’ (CBU) designation, with SUU-30H/B dispensers being paired with different payloads to form the CBU-58 and CBU-71 series. Contextual information suggests that this dispenser was part of a CBU-58/B cluster munition, but this cannot be established from an assessment of this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an aerosurface or ‘strake’ from a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) bomb guidance kit of the type fitted to MK 82-series 500-pound air-delivered bombs. The JDAM kits compatible with MK 82 bombs have aerosurfaces that are affixed near the nose of the bomb—rather than around the widest part of the bomb body, as seen in JDAM kits that are compatible with the larger MK 83 or MK 84 bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
MK 84 unguided air-delivered bombs can be fitted with a variety of tail kits, or with guidance kits which convert them into precision guided munitions (PGMs). When an air-delivered bomb impacts a building or the ground without functioning, the tail or guidance kit may be sheared off. With these separated from the munition—and in the absence of other identifying features, such as a seeker fitted to the nose of the weapon—it becomes very difficult to determine whether the bomb was guided or unguided. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The internal components of large, complex munitions often feature markings to aid in assembly, supply chain oversight, and quality assurance. In this case, a data plate marked with the name of the manufacturer (“MBDA FRANCE”) has been affixed to one of the rear control fins (“EQ, VENTRAL, FIN TIP”) of the missile. The NATO Stock Number (NSN) is also visible. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an actuator from a Storm Shadow-series missile. Actuators are components of guided munitions that are most often used to move control surfaces (e.g., fins and wings), enabling the munition to adjust its course in-flight in response to guidance commands. In this case, the component is fitted with a ‘data plate’ that indicates it was manufactured by MBDA France. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Microturbo TRI 60-30 turbojet engine from a Storm Shadow-series air-launched cruise missile. Further remnants of the rear of the missile are also visible, including one of the rear control fins. The Storm Shadow has a range of more than 250 kilometres. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rear of the second stage of the penetrator warhead (also called a ‘follow-through’ warhead) of the Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead system present in the Storm Shadow/SCALP-EG missile. The cylindrical object in the centre of the warhead (with a data plate marked “THALES”) is the fuze. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the first stage of the Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead used by the Storm Shadow/SCALP-EG missile. The BROACH uses a shaped-charge warhead (seen here) as its first stage, to help penetrate hardened targets, whilst the second stage comprises a conventional high explosive penetrator warhead (also called a ‘follow-through’ warhead) (ARES).
Analyst Note:
The remnant at left in this image is the second stage, or penetrator warhead, of the Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead as used in the Storm Shadow/SCALP-EG air-launched cruise missile. In this case, it has failed to function as intended. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, two GBU-39 guided air-delivered bombs can be seen in their shipping containers, with only the nose and the tail actuation section of the munitions clearly visible. Distinctive packaging such as this can sometimes be used as contextual evidence for the presence of specific munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This U.S. Department of Defense file photo shows an M142 High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) launching an MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) series tactical ballistic missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows part of a heavy-duty suspension lug associated with the Storm Shadow air-launched cruise missile. This is made clear from dot-peened markings which include “STORM SHADOW USE ONLY” and identifiers such as a NATO Stock Number (NSN). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The munitions remnant on the left of this image is part of a suspension lug associated with the Storm Shadow air-launched cruise missile, which is used to attach the munition to an aircraft. This component is of heavy construction, and as such often survives the missile’s functioning intact. This photograph purports to show remnants recovered from a Storm Shadow missile that was fired by Ukrainian forces into Russian territory, but this claim cannot be verified from the image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This MGM-140 cluster munition has failed to function as intended, and its payload of M74 submunitions is seen here spilling out of the warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
These R-122 ‘Grad’-type 122 mm surface-to-surface rockets were produced in North Korea. The example to the right is fitted with an F-122 impact fuze. Whilst a two-tone colour scheme is more common amongst those North Korean Grad rockets thus far identified in the context of the Ukraine conflict (these typically featuring a black forward section), uniformly coloured examples like this have also been identified previously. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Two of the distinctive, black tailfins used on S8-series air-to-surface rockets are visible to front and left of the remnant material. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a rocket motor section from an MGM-140 ATACMS series surface-to-surface ballistic missile. The warhead section of the MGM-140 series missiles separate from the rocket motor before functioning, resulting in the rocket motor often being found relatively intact near the target. The MGM-140 series missiles use the same rocket motor, preventing a positive identification of the variant based off the rocket motor alone, unless the variant markings are visible. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This remnant of an MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) surface-to-surface ballistic missile is marked to indicate it is the MGM-140A variant, a cluster munition which carries 950 M74 multi-purpose submunitions. Submunitions of this type are sometimes referred to by the acronym ‘anti-personnel and anti‑materiel (APAM)’. Additional markings indicate a manufacturing date (“10/96”; October 1996), a serial number (“411240”), and other information. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Almost all cluster munitions, including this example, expel their submunitions during flight. The submunitions are often held in an internal frame, such as that visible here, prior to being expelled. Depending on the munition, these internal frames may be diagnostic for identification. They usually do not carry a significant explosive payload in their own right, and therefore often withstand the functioning of the munition relatively intact. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Honeycomb-like internal structures are often used in aerospace applications to provide rigidity with reduced weight, and are sometimes constructed using materials which reduce radar cross-section by absorbing or scattering electromagnetic waves. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M27K3 surface-to-surface rocket is fitted with the 9N128K3 cargo warhead (seen here). This warhead carries a payload of 312 PFM-1 or PFM-1S scatterable anti-personnel landmines. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The markings on this 9N128K3 cargo warhead indicate that it was produced in 1989 and fitted to a 9M27K3 rocket in 1990. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The arming vane for a nose fuze (painted red) is visible on each of the two leftmost MAB-10B6 air-delivered bombs in this image. As the bomb falls, air passing over the arming vane causes it to spin, arming the fuze. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The circles in this image indicate where the fixed fin assembly is connected to the bomb body. Fin assemblies such as this help stabilise the bomb as it falls, improving the predictability of the trajectory and thus precision. Fins also orient the bomb as it falls so that munition travels nose-down. Orientation of the bomb on impact can play a role in fuze functioning, as well as the distribution of explosive or other effects. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Iranian 60 mm mortar projectile is of the ‘Long Range’ type described without a specific model name in various Iranian export catalogues and other sources. The designation as marked on projectiles and packaging is variable, with observed formulations including “60mm H.E. L.R.”, “60mm H.E L.R”, and “60mm HE L.R”. Sometimes, as here, “60mm L.R” is followed by “HE / TNT”. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Blue Sparrow-series air-launched ballistic missile is being carried by an F-15C fighter aircraft from 106 Squadron Israeli Air Force. The missile is marked with the logos of three organisations involved in its development—the U.S. Missile Defense Agency, the Directorate of Defence Research & Development, and the Israel Missile Defense Organization—and the Blue Sparrow programme logo of the manufacturer (Rafael Advanced Defense Systems). The booster section also features bright-orange fins and markings consistent with its use as a target missile, here modified to accept a high explosive warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Blue Sparrow is one of a series of three of air-launched missiles originally designed by Rafael as targets to test ballistic missile defence systems. Blue Sparrow missiles can be fitted with either inert or high explosive (HE) warheads. The recovery of Sparrow-series boosters following a reported Israeli strike on an Iranian air-defence system could suggest that a derivative variant of the Blue Sparrow missile was further developed for engaging surface targets. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows what is probably just the body of an Israeli 155 mm smoke artillery projectile. Israel predominantly uses two varieties of 155 mm smoke munition: the M825 white phosphorous (WP) series of munitions, and the M150 hexachloroethane/zinc mixture (HC) munition. These munitions are externally near-identical, save for their markings. In this case, the markings are insufficient to determine whether the image shows an M825-series WP munition or an M150 HC munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M22S is essentially the ‘full-sized’ version of the shorter 9M28S surface-to-surface rocket previously recorded in the OSMP. Both rockets carry the same 9N510 incendiary warhead, but differ in the length of their rocket motor sections, and thus range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9Н123К (9N123K) cargo warhead is delivered by a 9М79К (9M79K) series surface-to-surface guided missile. This cluster munition carries fifty 9Н24 (9N24) high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) submunitions, and is launched from the 9К79 Tochka series of tactical ballistic missile launchers. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
A 9N24 submunition is visible to the left of the 9N123K warhead in this image. This high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) submunition is marked to indicate it was produced in 1989 and filled with A-IX-2 explosive composition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Labels on munition remnants can provide a host of useful data, including the model designation (in this case, “GBU-39/B”), part number (PN; (“70P998100-1003”), National Stock Number (NSN; “1325-01-526-8728”), serial number (SN; illegible), and Department of Defense Identification Code (DODIC; “EC53”). These codes, and others like them, can often be searched for in databases or provided to technical specialists for further interpretation. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Stunner missile is the surface-to-air interceptor missile fired by the David’s Sling weapon system to defeat short-range ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, drones, and rockets. The Stunner does not carry an explosive warhead, instead relying on kinetic impact (also called the ‘hit-to-kill’ principle) to intercept ballistic missiles and other targets. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M28S surface-to-surface unguided rocket carries the 9N510 warhead, which disperses burning thermite-type incendiary elements over a wide area upon functioning. This munition is designed to start fires in target areas vulnerable to incendiary attack, including forests, ammunition dumps, and fuel storage sites. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This M107 high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectile is fitted with an RT180 multi-function fuze. The RT180 can be set to operate in point-detonating or proximity modes. The factory setting for the proximity fuze detonates the warheads an average of 9 metres above the target. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows most of the forward half of a Tamir surface-to-air missile, including the guidance section and warhead, as fired by launchers in the Iron Dome system. These interceptor missiles are fast and manoeuvrable with a relatively small explosive payload. Their construction and low yield means that remnants are often recovered largely intact. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The RAFAEL Advanced Defense Systems SPICE 1000 guidance kit is fitted to MK 83-series 1,000-pound unguided air-delivered bombs to convert them to precision guided munitions. Like the JDAM-ER, it has a deployable wings to provide a ‘gliding’ attack trajectory. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The BLU-117 air-delivered bomb is nearly identical in format to the more common MK 84, but uses the PBXN-109 explosive filler which is more insensitive than the typical explosive compositions found in MK 80-series bombs. The BLU-117 is also coated with a grey, thermally resistant paint, and marked with three yellow bands (as opposed to the green paint with two yellow bands found on standard MK 80-series bombs). These changes were requested by the U.S. Navy for safer storage of these munitions aboard ships. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This 9M27K-series surface-to-surface cargo rocket is carrying a payload of 9N210 or 9N235 high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) submunitions. These submunitions are difficult to distinguish unless their external markings are visible, or a close examination is made. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The visible component is part of a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) guidance kit, an accessory package that is fitted to unguided air-delivered bombs to convert them to precision guided munitions. Specifically, this image shows a control fin from the tail assembly. Whilst the JDAM kit would not constitute a munition in its own right, this remnant is included in the OSMP as contextual information strongly suggests it formed part of a complete munition that functioned. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
The JDAM-ER in this photograph is affixed to an unusual pylon thought to be of Ukrainian design, which allows the Western munition to be carried by the Soviet-designed Mikoyan MiG-29 and Sukhoi Su-27 fighter aircraft in service with the Ukrainian Air Force (a MiG-29 is pictured here). (ARES)
3 Analyst Notes:
This is an image released by the Israeli Defense Forces that shows an F-15I of 69 Squadron Israeli Air Force preparing to take part in a high-profile airstrike on 27 September 2024, in which the leader of Hezbollah, Hassan Nasrallah, was killed.
Analyst Note:
The MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) series includes variants with a variety of different payloads, including submunitions and unitary high explosive (HE) warheads. The number of submunitions carried and effective ranges also vary.
Ukraine has reportedly received the MGM-140A and MGM-140B variants, which are externally visually identical and must usually be distinguished by markings. The MGM-140A carries 950 M74 submunitions, with an effective range of 165 km, while the MGM-140B carries only 300 M74 submunitions but has a longer effective range of 300 km. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M117 series of air-delivered bombs were historically referred to as ‘demolition bombs’, due to the more substantial blast effect they offer in comparison with so-called ‘general-purpose bombs’. This is achieved through the use of more energetic explosive compositions, such as Tritonal or Minol, which incorporate an oxidiser (typically aluminium powder). Today, munitions using such compositions are sometimes considered in the loose category of ‘enhanced blast munitions’, but the distinction between demolition and general-purpose bombs has largely disappeared. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The crude launch arrangement depicted in this photograph shows the ease with which many simple rocket designs can be launched. Weapons such as this are used where precision fire is not a requirement; i.e., where the target might be a whole compound, neighbourhood, or settlement, rather than a specific building or vehicle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M824 60 mm mortar projectile dispenses a parachute-retarded illumination flare which burns for 35 seconds. The tail portion of the munition (seen here) separates from the forward (body) portion and is sometimes found along the line of fire. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This is an Iranian 60 mm mortar projectile, marked to indicate it is of the ‘high explosive, long-range’ type (“H.E L.R”). Both the munition body and fuze are marked to with the year of production (“2008”). Whilst the tan colouring is often indicative of Iranian-made munitions (especially where the fins are also painted), this is not diagnostic, and a combination of physical features and markings should be assessed to reach a positive identification. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Contextual information, including an assessment of the crater which appears to be linked to this munition remnant, suggests that a 2,000-pound-class bomb fitted with a SPICE 2000 guidance kit was used in this airstrike. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Israeli Air Force F-16C fighter aircraft from 101 Squadron carrying a MK 84-series 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bomb fitted with a SPICE 2000 ‘bolt-on’ guidance kit. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
These are munition debris images released by the Israel Defence Forces and are not necessarily in situ. (Airwars)
Analyst Note:
These are munition debris images released by the Israel Defence Forces and are not necessarily in situ. (Airwars)
Analyst Note:
These are munition debris images released by the Israel Defence Forces and are not necessarily in situ. (Airwars)
Analyst Note:
Markings on this 106 mm recoilless gun projectile indicate it is a M344A1 high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) round (“CH-106-M344-A1”) produced by Fábrica Nacional de Granada (“FNG”), Spain, in 1984 (“84”). The packing crate identifies the intended weapon as an M40A1 Cañón sin retroceso, or ‘recoilless rifle’ (“C.S.R. 106 M40 A1”). Other markings show that the round is fitted with an M509-type point-impact, base initiating (PIBD) fuze (“Espoleta PIBD M509”), and give additional details such as the expected muzzle velocity (“V₀”) of 503 m/s. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Iranian M91 81 mm mortar projectile is marked to indicate it was produced in 2009. The AZ111A2 fuze fitted to the projectile is also marked with the same year of manufacture. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M14 Malyutka anti-tank guided missile was designed and fielded by the Soviet Union in the 1960s. It uses an outdated guidance principle known as manual command to line-of-sight (MCLOS), in which the operator must manually adjust the course of the missile in flight. Nonetheless, this munition has been seen in several 21st-century conflicts. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, an F-15C fighter aircraft from 106 Squadron Israeli Air Force is seen carrying two MK 84-series 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bombs fitted with Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) ‘bolt-on’ guidance kits. In U.S. service, this combination is known as the GBU-31. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the nosecone from an Israeli Tamir surface-to-air missile. This component is often found as a remnant after the functioning of the missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The AGM-179 Joint Air-to-Ground Missile (JAGM) is derived from the AGM-114 Hellfire series of air-to-surface missiles—and thus shares physical characteristics in terms of general construction, including rear fin placement. The marked weight of 52.0 kg (115 lbs) is generally believed to be an indicator that the rocket motor is from a JAGM; however, remnants marked with this weight have been observed from several years before the JAGM was initially fielded. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, four AGM-114 Hellfire-series missiles can be seen fitted to an M299-series missile launcher, itself attached to the stub wings of this Israeli AH-64 Apache helicopter. In theory, the Apache could be armed with up to sixteen Hellfire missiles, but fewer are carried in practice to allow for other weapons and sensor payloads (ARES).
Analyst Note:
‘Khaibar-1’ is a designation given to a series of 302 mm rockets produced in Syria, possibly derived from the Chinese WS-1/WS-1B. The Khaibar-1 is also referred to as the M-302 or M302. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Iranian M48 120 mm mortar projectile is marked to indicate it was manufactured in 2008. A plastic bag cable-tied to the tail of the munition protects the auxiliary, or supplemental, propellant charges fitted to the round. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
These M485 series 155 mm artillery gun projectiles are painted yellow to indicate their functional type: illumination rounds. The M485 series of illumination projectiles are base-eject munitions that expel a parachute-retarded illuminant canister which casts light over the battlefield as it descends. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Iranian copy of the Chinese Type 63 107 mm rocket is marked with a red stripe and text to indicate it is of the high explosive incendiary (“H.E.I”) type. Markings also show that it was produced in 2007. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The physical features, colour scheme, and packaging of these 120 mm mortar projectiles are all consistent with Iranian manufacture, but the markings are mostly obscured in this image. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Joint Direct Attack Munition – Extended Range (JDAM-ER) marries the JDAM guidance kit to a ‘glide bomb’ wing kit developed by the Australian Defence Force, offering a munition with at least three times the range of a standard GBU-38 500-pound-class guided aerial bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, two GBU-39 Small Diameter Bombs are attached to a BRU-61/A bomb rack. The Ukrainian Air Force adapted this American-designed bomb rack to fit their Soviet-designed Mikoyan MiG-29 fighter aircraft. The BRU-61/A can carry up to four GBU-39 air-delivered bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Tamir Interceptor is the missile fired from Israel’s Iron Dome defence system to intercept incoming rockets, missiles, projectiles, and unmanned aerial vehicles (‘drones’). The Tamir uses a warhead with a relatively small explosive yield, which typically results in the guidance section, nosecone, and (spent) rocket motor falling to the ground relatively intact after functioning. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This is an Israeli 120 mm tank gun round, of the ‘armour-piercing, fin-stabilised discarding sabot – tracer’ (APFSDS-T) type. The physical features identify it as either the M322 or M338.
The projectile (penetrator) of this round has no explosive content and relies on kinetic energy to penetrate armoured targets. When a projectile is of a smaller calibre than the gun’s bore, a sabot is sometimes used to ensure the projectile is centred in the bore and to trap the gas from the propellant of the cartridge and propel the projectile. In flight, the sabot separates into two or more pieces, sometimes called ‘petals’, often found along the line of fire before the impact point. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Some tank gun projectiles may have fins affixed to an extended ‘tail boom’, in a similar manner to a mortar projectile. Note, however, that the cylindrical tail assembly is not perforated as it would be for most mortar projectiles. Tank gun projectiles are also more likely to be generally cylindrical, rather than lachrymiform (teardrop-shaped). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M329 is a multi-purpose tank gun projectile designed to engage a range of targets other than tanks. It is one of the few cluster munitions that takes the form of a tank gun projectile, dispensing six explosive submunitions over a relatively small area. It has also been referred to as the ‘APAM 120’, describing its functional role (‘anti-personnel/anti-materiel’) and calibre (120 mm). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, part of the distinctive internal 'X-rib' arrangement is visible protruding from the base of an M825-series white phosphorus smoke projectile. This is a useful diagnostic feature that can be used to distinguish remnants of these munitions from those of similar projectiles (such as those using a hexachloroethane/zinc smoke composition) if markings are not visible (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The remnants shown in these linked images have been falsely identified in Russian sources as chemical munitions. This image clearly exhibits the marking “NBK DM 1216”—the ‘NBK’ standing for the German Nebelkörper (‘smoke element’)—identifying this as one of four DM 1216 hexachloroethane/zinc (HC) smoke elements dispensed by the German DM 105 155 mm artillery gun projectile. Video of the incident shows all four elements being ejected from the base of the projectile in flight. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a distinctively shaped component of MBDA’s ‘Diamond Back’ joined tandem wing assembly as fitted to the GBU-39 Small Diameter Bomb (SDB). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The SPICE family of munitions, manufactured by Israeli aerospace and defence company Rafael, includes two models which use ‘bolt-on’ guidance kits. The SPICE 1000 and SPICE 2000 models convert 1,000- and 2,000-pound unguided aerial bombs, respectively, to precision guided munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a component believed to be part of the folding-blade assembly used in the AGM-114R-9X variant of the Hellfire missile. Blades are used in place of an explosive payload to create a kinetic weapon that achieves a practical level of lethality whilst minimising collateral harm. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Israeli illumination munitions—often finished in a distinctive yellow—are sometimes mistaken for high explosive munitions by observers more familiar with the NATO or U.S. marking systems. This image shows an M485-pattern illumination projectile, a base-eject type that uses a parachute-retarded canister containing a powerful candle to illuminate the battlefield.
Analyst Note:
Little is known with certainty about the AGM-114-R9X variant of the Hellfire missile, although it has been associated with high-profile targeted killings including those of senior al-Qaeda figures. The weapon functions as a kinetic-impact munition, using pop-out blades—rather than an explosive warhead—to reduce the prospects of collateral harm. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M825A1 155 mm smoke projectile makes use of white phosphorus (WP) to generate a brilliant white smoke. Whilst WP does have incendiary effects, the method of dispersal in the case of the M825A1 is optimised for screening and marking purposes. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The remnant pictured here is part of a Small Diameter Bomb actuator assembly (‘Tail Actuation Section’), which moves the four tail-fin control surfaces which alter the course of the munition in flight. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image depicts either a 9M27K or 9M27K1 cargo rocket (cluster munition). The 9M27K carries the 9N210 high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) submunition, whilst the 9M27K1 carries the 9N235 HE-FRAG submunition (ARES).
Analyst Note:
The circled remnant is the hardened steel nosecone of the GBU-39, which renders the munition capable of penetrating more than 3 feet (approx. 1 metre) of steel-reinforced concrete. It is one of several components that often survives the detonation of the munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image depicts an M117-series unguided aerial bomb. Belonging to a class of weapons referred to as ‘demolition bombs’—which use Tritonal or similar explosive compounds to generate a more powerful blast effect than TNT or Composition B—the M117 is an American design which dates to the Korean War era and is rarely seen in service with modern armed forces. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Contextual information suggests that this is likely a 9M22S unguided incendiary rocket (see External Research section), but this cannot be confirmed on the basis of this image alone. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
This munition is assessed to be one of the Small Diameter Bomb (SDB) I variants (GBU-39 series), rather than one of the SDB II 'StormBreaker' (GBU-53 series) munitions, on the basis of contextual information. 'Small Diameter Bomb' is the manufacturer's terminology, whilst 'GBU-39' is the U.S. Air Force designation (also used by many other operators). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Some artillery projectiles, such as this M150 type, use a hexachloroethane-based composition (HC) to generate smoke for screening or marking purposes. In many armed forces, HC smoke munitions have partially replaced those relying on white phosphorus for similar effects. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
107mm spin-stabilized rockets of this design are often utilized by non-state actors in an indirect fire role. Like the original Chinese models that they are copied from, they do not require more than a simple electric power source and a rudimentary launch platform to achieve an acceptable level of accuracy. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The various Iranian Qaem-series guided air-delivered bombs can be difficult to differentiate from one another. In this case, the wing (forward fin) assembly distinguishes this Qaem-5 from the visually similar Qaem-1. Note also that the name 'Qaem' has applied by Iran to other, unrelated munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Once fired, four canards will deploy from the forward (ogival) section of these M982 Excalibur guided artillery projectiles. The narrow-shaped ports through which the canards deploy are a good indicator of a guided or extended-range artillery projectile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Many guided (or otherwise complex) munitions like this one are marked with additional information on individual assemblies or components. This can include information on sub-contractors that produced or integrated specific parts of a munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, a Ukrainian soldier is using an M1155 Enhanced Portable Inductive Artillery Fuze Setter (EPIAFS) to input the target coordinates and set functioning parameters for an M982 Excalibur guided artillery projectile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The MK 84 series of unguided air-delivered bombs can be converted to precision guided munitions by being fitted with guidance kits such as the Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM), SPICE 2000, or Paveway series. This MK 84 is also marked with a variant designation “MOD 4”. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The image is of "a high-velocity shell fired from the main armament of a battle tank," Desmond Travers, former director of the Institute for International Criminal Investigations, told Airwars and AFP. "The calibre appears to be 120 mm, and the shell is fin-stabilised. The maximum effective range is five kilometers, but a skilled tank crew member should be able to hit a target the size of a car." (Airwars)
Analyst Note:
The M-54 ‘high-drag’ series of Soviet/Russian air-delivered bombs can be distinguished by two key identification features: 1.) the ballistic ring located in the forward portion of the bomb (missing in this example); and 2.) the presence of two or four rectangular, longitudinal ‘levelling bars’ (two can be seen in this example). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Russian air-delivered cluster bombs, such as this one, are often named using a designation that is a compound of the names of the cargo (carrier) bomb and the submunition it carries. For example, this RBK-500 unguided, air-delivered cluster bomb carries 268 PTAB-1M HEAT submunitions, and is thus designated the 'RBK-500 PTAB-1M'. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This component is one of four pneumatically controlled canards from the guidance section of a Paveway II precision guided munition (PGM) conversion kit. When a Paveway II conversion kit is fitted to a MK 82 series unguided air-delivered bomb (note markings), the munition receives a GBU-12 series designation. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 57E6 series of missiles fired from the 96K6 Pantsir system use a two-stage design that is unusual for surface-to-air missiles of this type. The remnant seen in this image is part of the missile’s booster section, which accelerates the second stage to a high velocity before separating. The booster section uses a distinctive toffee-brown, filament-wound composite body. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Cargo rockets often use an internal frame to manage the correct carriage and expulsion of submunitions. These internal frames frequently survive largely intact after the munition has functioned, and may be diagnostic in identifying a munition by type, series, or model. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Although this munition started out life as a mortar projectile of the M492-pattern, it has been modified to be dropped from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and, in its present state, could not be fired from a conventional mortar. As such, it is correctly classified here as an air-delivered bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The fin assembly in the image bears a strong resemblance to those of other munitions employed in the same incident that have been identified as M49A2 mortar projectiles modified to be delivered by UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The large fragments in this image are typical of 'natural' fragmentation resulting from the rupturing of a thick-walled munition (in this case, an artillery projectile) by the functioning of its explosive payload. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image features both delivered (the two left-most munitions) and undelivered munitions of the same model.
Analyst Note:
Like the more common 9M22S rocket, the 9M28S carries the 9N510 warhead, which dispenses 180 individual incendiary elements composed of a magnesium alloy shell filled with a thermite-like incendiary composition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Brimstone is a series of British-designed guided missiles that can be launched from air, land, or sea platforms. The United Kingdom first provided Ukraine with the Brimstone I missile in 2022 and exports have continued since, more recently believed to include the Brimstone II model. In Ukraine, Brimstone-series missiles have been exclusively launched from ground-based and sea-based platforms as of May 2024. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
122 mm ‘Grad’ rockets can be fired from a variety of launchers and even in improvised ways. The most common is the BM-21 launcher and its later derivatives, but many other portable or vehicle-mounted launchers have been used around the world. Craft-produced examples—ranging from simple rails to more complex designs comparable to factory made launchers—are also common. In some cases, Grad rockets are even fired whilst supported by a crude arrangement of logs, bricks, or rocks. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This artillery projectile is a non-lethal type designed to carry propaganda leaflets. Externally, it strongly resembles other variants carrying lethal payloads, although this particular model has a distinctive all-red colour. The leaflets are expelled from the base of the munition by the action of a small explosive charge, after a set amount of time has elapsed after firing (determined by the fuze). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
These S-25-O air-to-surface rockets are each loaded into a single-barrelled O-25 rocket launcher (sometimes called a 'launch tube' or 'rocket pod') that is affixed to an aircraft hardpoint. The over-calibre high explosive fragmentation warhead (of 420 mm in diameter) protrudes from the front of the tube. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
As a result of the rapid introduction of new models and variants during ongoing conflicts, sometimes a munition is issued with a provisional designation, or with no designation at all. In other cases, the designation is not yet known to researchers. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Whilst most mortars are smoothbore guns, some have a rifled bore. These M1101 120 mm mortar projectiles feature a 'pre-rifled' driving band—that is, a driving band with grooves cut at the factory to fit the mortar's rifling. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Not all munitions have a lethal purpose. This is a type of ‘carrier’ or ‘cargo’ munition designed to carry and dispense a non-lethal payload—in this case, propaganda leaflets. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
The plum-coloured plastic ring at the nose of this mortar projectile (placed over its fuze) and the black plastic propellant cover (placed over its tail) are both fitted for transport and storage, before the projectile is loaded into a cardboard tube, and then packed into an outer crate. The propellant cover obscures the perforated cylindrical tail assembly in this image. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image depicts a Ukrainian-made version of the Soviet-era OF-25 152 mm artillery projectile, the designation of which is not publicly known at this time (May 2024). The yellow base colour was commonly found in batches produced by Ukroboronprom in late 2022. Later batches returned to a grey base colour. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The OF-NMR is a rocket-assisted mortar projectile, which uses a solid-fuel rocket motor located in the cylindrical portion of the body, below the ogive, to extend its range. Rocket-assisted mortar projectiles are rarely encountered. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The “+” marking is a weight classification symbol which indicates standard deviation. One “+” sign indicates a deviation from 0.33% to 1.00% of the stated weight. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Whereas many cartridges are of the 'fixed' type—with the propellant charge contained entirely within the cartridge, and the cartridge case crimped around the projectile—the OF-540 artillery gun projectile is a type of 'semi-fixed' ammunition. A round of semi-fixed ammunition is separated into two groups of components: the projectile and fuze; and the cartridge case, primer, and one or more propellant charges. These two component groups are typically combined at the time of loading the gun, or shortly beforehand. The majority of ammunition fired by artillery systems is either semi-fixed or 'separate loading' (see Glossary). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 120 mm 3-Z-2 incendiary mortar projectile contains 6 incendiary elements, four large and two small. These are hollow steel ‘cups’ filled with an incendiary mixture of an unknown type, but understood to be comparable in effect to thermite. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The AGM-88 High-Speed-Anti-Radiation-Missile (HARM) is an air-to-surface anti-radiation guided missile that seeks and destroys radar-based air-defence systems by detecting radar emissions, locking on to these, and using them to home in on a target. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a 9M27K2 cargo rocket as well as several partially ejected PTM-1 anti-vehicle landmines. This 9M27K variant is fitted with the 9N128K2 payload section which carries and dispenses 24 PTM-1 mines. Other variants carry different mines or submunitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Next-generation Light Anti-tank Weapon (NLAW) uses an uncommon form of guidance known as predicted line-of-sight (PLOS). PLOS guidance calculates the anticipated position of a moving target prior to launch, with the munition using inertial guidance to fly to the projected impact point. This fire-and-forget technique allows the operator to move positions immediately after firing, and is generally cheaper than other fire-and-forget guidance types. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the control section from a 9M83-series surface-to-air missile. The 9M83 is launched by the Russian S-300V air defence system. The system and its missile have received the NATO designation ‘SA-12A Gladiator’. Missiles launched by air defence systems are often referred to by the name of the respective complete platform, rather than the specific model of the missile itself. For example, ‘S-300’ or ‘S-300V’ rather than ‘9M83’. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In the Ukraine conflict, several groups have offered a service whereby financial supporters can have a message of their choice marked on a munition. Such messages are often references to memes or popular media. The middle artillery projectile shown here is marked with “omae wa mou shindeiru”—an English transliteration of the Japanese phrase お前はもう死んでいる (“you are already dead”), which appears in the popular Fist of the North Star manga and anime series. (ARES)