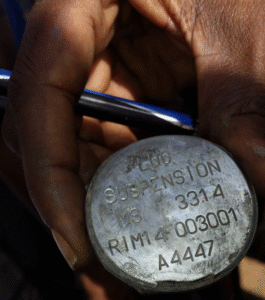Analyst Note:
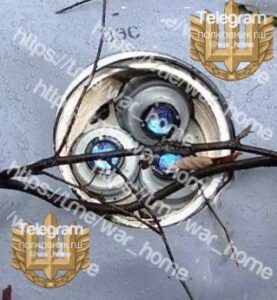
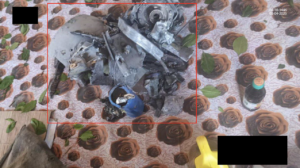
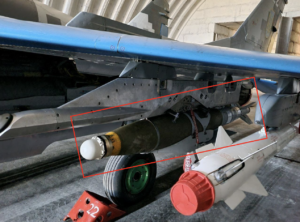
This image shows a fragment of the wing assembly of a Paveway bomb guidance kit. The data plate, though damaged, provides additional information about the munition. A partial Commercial and Government Entity code (CAGE; “ …14”), manufacturing part number (MFG SKU; “872127-1”), National Stock Number (NSN; “...5-01-141-5890”), serial number (Serial NO; 15-005326), and date of manufacture (“…MFR. 10/15”) are visible. This data can be used to look-up the component and determine that this specific fragment is from a Paveway II guidance kit intended for use with a MK 82-series 500-pound-class air-delivered bomb. This bomb and guidance kit combination is referred to as the GBU-12. The CAGE code, although partial, is enough to determine that this specific kit was produced by Raytheon, rather than the other known manufacturer of the Paveway kits, Lockheed Martin. (ARES)
 Rely on the rapid expansion of gases released by a detonating high explosive compound inside the munition to generate explosive power
Rely on the rapid expansion of gases released by a detonating high explosive compound inside the munition to generate explosive power