Analyst Note:
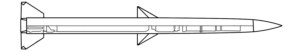
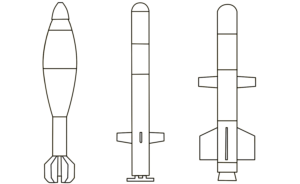
The UMPK guidance package is a ‘bolt-on’ kit that can be fitted to unguided air-delivered bombs to convert them to guided munitions. The UMPK kit also greatly extends the range of the munition to which it is fitted, allowing aircraft to strike from beyond the range of many air-defence systems. Currently only Russia manufacturers and uses these kits. (ARES)