Analyst Note:
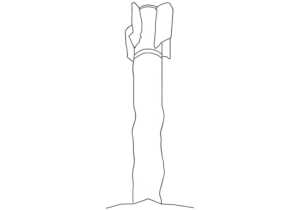
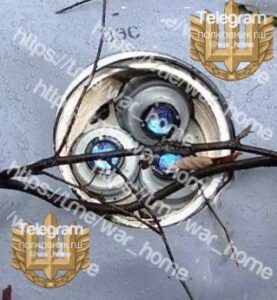
This image shows a fragment of the wing assembly of a Paveway bomb guidance kit. The data plate, though damaged, provides additional information about the munition. A partial Commercial and Government Entity code (CAGE; “ …14”), manufacturing part number (MFG SKU; “872127-1”), National Stock Number (NSN; “...5-01-141-5890”), serial number (Serial NO; 15-005326), and date of manufacture (“…MFR. 10/15”) are visible. This data can be used to look-up the component and determine that this specific fragment is from a Paveway II guidance kit intended for use with a MK 82-series 500-pound-class air-delivered bomb. This bomb and guidance kit combination is referred to as the GBU-12. The CAGE code, although partial, is enough to determine that this specific kit was produced by Raytheon, rather than the other known manufacturer of the Paveway kits, Lockheed Martin. (ARES)