257 results
Analyst Note:
This image shows a one-way-attack (‘sacrificial’) UAV with the apparent warhead broken off. It is believed to have been attached to the grey mechanism located at the rear of the UAV, likely separating when the UAV was downed. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mk 104 Dual Thrust Rocket Motor (DTRM), the second-stage rocket motor for the SM-2, SM-3 Blk I, and SM-6 missiles. Based on the strakes or fins attached to this Mk 104, it can be determined that it was part of an SM-3 Blk I series missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image provides a close-up view of the bottom of the MK 136 Third Stage Rocket Motor section from a RIM-161 Standard Missile 3 (SM-3) Blk I guided missile. The integral warm gas/cold gas attitude control system, including its four venturis, is visible. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the MK 136 Third Stage Rocket Motor of a U.S. RIM-161 Standard Missile 3 (SM-3) Blk I interceptor missile. The SM-3 Blk I variants share the same propulsion sections, but have differences in the kill vehicle section. The SM-3 Blk II variants are substantially different, including new, larger-diameter propulsion sections. SM-3 missiles have a booster, dual-thrust rocket motor, third-stage rocket motor, and an altitude control section in the kill vehicle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a one-way attack (OWA) UAV fitted with a high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead adapted from a PG-7 series recoilless gun projectile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This sheet-metal body component is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR-59518”) which indicates it was produced by GlenDee Corp. of Moorpark, California, which does business as Metalagraphics, Inc. (MGI). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Moog Inc.—headquartered in East Aurora, New York, as marked on this munitions remnant—describes itself as a “worldwide designer, manufacturer, and integrator of precision control components and systems”. Moog supplies actuator and control components to the prime contractor on the Miniature Air-Launched Decoy (MALD) programme, Raytheon. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This guided munition is built around a sacrificial DJI Avata-series UAV that has been fitted with an improvised explosive device (IED). From front to back, it consists of an impact switch made from a syringe, the main charge (yellow/white material in a plastic bag), and a battery that acts as the power source. While crudely made, it is probably still functional. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this case, the tentative identification of this munition is possible based on an analysis of its silhouette, particularly the distinctive detachable warhead compartment that can be seen hanging from the base of the munition's body. In many cases, such an identification technique would not be possible to apply with confidence. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the venturi and tailfin assembly from a 57 mm S-5 series rocket. The S-5 series of rockets are commonly used around the world in a variety of roles, including air-to-surface and surface-to-surface. Unfortunately, from this image alone the specific model and country of origin cannot be determined. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
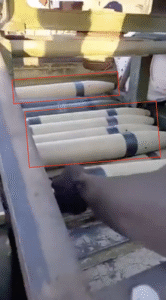
This image shows several 107 mm rockets of the Type 63 pattern. Whilst developed by China, munitions of this design are now produced by several countries around the world, including Iran, North Korea, and Sudan. The state-owned Military Industry Corporation (MIC) of Sudan produces a copy of the Type 63 known as the TAKA-01, TAKA-1, or TAKA-107. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the damaged rocket motor section of a ballistic missile that was fired by the Houthis in Yemen towards Israel and likely intercepted. The Houthis employ ballistic missiles that are supplied by Iran, and given different names. In Houthi service, the Iranian Kheibar Shekan missile is known as the Hatem-2. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the TRDD-50A(M) (ТРДД-50А(M)) turbojet engine, which powers Kh-101 and Kh-59M missiles. Other models of Russian cruise missiles are known to use other variants of the TRDD-50. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The image shows a one-way-attack (OWA) UAV that appears to have crashed, but failed to function. It consists of an FPV chassis, as well as some of the essential components required for flight and the explosive charge (purple container). The initiator and other parts relevant to both flight and the munition’s function are not visible. This appears to be craft-produced ‘sacrificial’ UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This photo shows some of the lithium-ion power banks found within a Gerbera UAV. These are used to power the onboard avionics, control surfaces, communications hardware, camera, and other components. The quantity and type of batteries fitted to the Gerbera will often vary based on the role for which the UAV has been configured—one-way attack (OWA; i.e., a ‘sacrificial’ munition), reconnaissance, signal relay, or decoy—and which specific hardware has been installed to effect this mission. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This photo shows the fuel bladder of a Gerbera UAV, which still contains some fuel. It is likely that a bladder is used—rather than a rigid tank—to save on both weight and cost. Some variants of the Gerbera have been observed to be fitted with a second bladder in the forward section of the fuselage, serving to extend the UAV’s range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
A Gerbera-series UAV is pictured here being carried by just two Ukrainian soldiers. This highlights the Gerbera’s lightweight design—the airframe is mostly constructed from Styrofoam and wood, which saves on both weight and cost. This particular example does not bear signs of significant damage, suggesting that it either malfunctioned or was brought down by EW and crashed. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an A40 Pro camera, manufactured by the Chinese company Viewpro UAV and design specifically for use in UAVs. The black box to the right of the camera is the control box which manages video output, camera control, and power. The manufacturer claims this model has a 40× optical zoom, AI detection and tracking, and 3-axis gyro-stabilisation. The company further claims that it can customise the onboard AI recognition based on “target characteristics” provided by the client. Numerous Gerberas fitted with this model of camera are known to have been recovered by Ukrainian forces, although it is by no means the only camera model in use. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the back surface of a wireless communications module contained within a downed Gerbera UAV. Although labeled as an HX-50 model designed for fixed locations, Ukrainian military analysis indicates this is an XK-F358 mesh-network module more suitable for use in UAVs. See OSMP1646 for further details. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the front and interior surfaces of a wireless communications module recovered from a downed Gerbera UAV. Although labelled as an HX-50 industrial wireless modem (compatible with WiFi and 5G/4G networks and designed for fixed locations), analysis by Ukrainian military sources indicates that this component is, in fact, an XK-F358 mesh-network module which offers significantly more capabilities. Manufactured and sold by Shenzhen Xingkai Technology Co., Ltd., these modules are designed for, amongst other things, use in robots and unmanned vehicles. Gerbera UAVs have been found operating on a wide variety of frequencies and networks, and this type of module is well-suited to this use. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Israeli-made 122 mm rocket motor found following a strike on Amr School in Gaza City. Although it is not possible to be definitive from this image alone, it is likely that this rocket motor was part of an Israeli ‘Bar’ missile, a guided munition designed for precision strikes in urban areas that uses a 122 mm rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows remnants of two different rocket motors from AGM-114 series Hellfire missiles. While it cannot be determined by these entries alone, images of the damage from the strike associated with this image, gathered by Mwatana, indicate that both of these AGM-114 missiles were the kinetic AGM-114R9X variant. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the top of the booster of an Arrow 3 interceptor missile, where it connects to the kill vehicle. The Arrow 3 was jointly developed by the United States and Israel, and first entered service in 2017. The date of manufacture marking (“DATE OF MFG: 05/2018”) indicates that this booster was produced in the year after the Arrow 3 first entered service. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the booster of an Israeli Arrow 3 interceptor missile. The Arrow 3 is designed to engage ballistic missiles and is capable of exo-atmospheric interceptions. Once the booster is expended, it separates from the ‘kill vehicle’. The kill vehicle has a sustainer motor that propels it towards the incoming ballistic missile, and uses kinetic impact, rather than an explosive warhead, to disable or destroy its target. This is sometimes called the ‘hit-to-kill’ principle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rocket motor of an AGM-114 "Hellfire" series guided missile found in Jordan during the 12 day conflict between Israel and Iran. This specific Hellfire missile is likely an air-to-air "C-UAS" variant used to intercept one-way attack drones, such as those launched by Iran towards Israel, rather than the more common air-to-surface Hellfire missile variants. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mikholit that was ejected from the weapons pod of an Israeli Hermes 900 drone that was downed in Iran. This Hermes 900 drone had two weapons pod, each capable of carrying 4 Mikholit bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a variety of small air-delivered munitions that have been developed specifically for deployment via UAV. Some of these appear to be original designs, whilst others have been made by modifying existing munitions. This entry reflects those munitions outlined with the red box, but all of the munitions are generally of similar in size and format, and all have tailfin assemblies intended to orient the munition as it falls, just like more traditional air-delivered bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows three sets of three PTM-1 series scatterable anti-vehicle mines taped together. While these mines have likely been repurposed from their original delivery munition to be delivered via UAV, this cannot be confirmed based off this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the nosecone from an Israeli SPICE 250 air-delivered bomb. Whilst generally similar in appearance to the nosecone of the GBU-39, the SPICE 250 nosecone is longer and narrower. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the flare from a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system's ‘Talon’ kinetic interceptor missile. The flare is located at the aft end of the missile's booster engine. The ‘petals’ of the flare are initially flush, and are actuated into the deployed position, seen here, as part of the missile‘s functioning. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mikholit glide bomb, with its warhead removed (green cylinder on the left side of the box). The fins that spring outward when deploye have been taped down. This Mikholit was reportedly recovered by the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) from Hamas, who had captured the bomb after it failed to function when originally deployed by the IDF. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two Mikholit air-delivered bombs (‘glide bombs’), and four Mikholit warheads. There are at least two different variants of warheads available for the Mikholit glide bomb. The green cylinder on the left is a blast (high explosive) warhead, whilst the other three warheads are shaped charge warheads which incorporate additional fragmentation. Blast warheads of this type have also been seen with red markings, while the shaped charge warheads have been seen with yellow markings. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rear fin section that is attached to a M-302/Khaibar-1/Fadi series rockets to add guidance capabilities. This rear fin section is installed, along with a forward control section between the warhead and the rocket motor. The guided munition, now classified as a missile, is referred to as a Nasr-1/Nasr-2. A similar, but larger, rear fin section is fitted to Zelzal rockets to convert them to guided munitions. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rocket motor of a Kheibar Shekan or Fattah-1 medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM). The Fattah-1 was publicly unveiled by Iran in June 2023, with very few images surfacing since that time. Due to the lack of available reference material, differentially identifying the Kheibar Shekan and Fattah-1 is difficult. The missile components displayed at unveilings and public displays are also often different from those used in production models. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Iranian M344 106 mm recoilless gun projectile. The M344 is a high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) munition, containing a shaped charge that is designed to penetrate armour. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Two R-77 air-to-air missiles (NATO reporting name: AA-12 Adder) are carried in this photograph by a Russian Aerospace Forces Sukhoi Su-35 fighter aircraft. Key markings, including the aircraft’s bort number (a coloured numeral that acts as a unit or base identifier), have been digitally obscured. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Armement Air-Sol Modulaire (AASM; ‘Modular Air-to-Ground Armament’) family of French bolt-on guidance kits are fitted to air-delivered bombs of various sizes in a similar fashion to American JDAM kits. In some marketing materials, the acronym HAMMER is used, standing for ‘Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range’. This refers, in part, to the rocket boosters fitted to munitions in the family to extend their effective range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this photo, a Ukrainian Sukhoi Su-25 ground-attack aircraft from the 299th Tactical Aviation Brigade, with the bort number ‘Blue 28’, is seen carrying an AASM-250 guided air-delivered bomb under its left wing. Available imagery shows that the AASM-250 has also been fitted to Mikoyan MiG-29 fighter aircraft, and can likely be carried by the Sukhoi Su-27 as well. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Contextual images of the damage caused by this munition indicate the remnant pictured is from the AGM-114R9X variant of the Hellfire missile, a kinetic munition which does not carry an explosive warhead. This remnant cannot be differentiated from either other AGM-114 or the AGM-179 JAGM variants based off this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M712 ‘Copperhead’ is a laser-guided 155 mm artillery gun projectile carrying a high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead designed to engage armoured vehicles. The Copperhead was developed in the United States in the 1970s, and saw limited use during Operation Desert Storm. The M712 is is pictured here inside its shipping container, and the slots for the enclosed, deployable (‘pop-out’) wings and fins are visible. The M712 has two operational modes: a ballistic mode that follows a gun’s ballistic trajectory like a traditional artillery projectile, and a glide mode, which follows a longer and flatter trajectory. The preferred mode is set by the artillery crew before firing. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Two of the distinctive, black tailfins used on S8-series air-to-surface rockets are visible to front and left of the remnant material. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Honeycomb-like internal structures are often used in aerospace applications to provide rigidity with reduced weight, and are sometimes constructed using materials which reduce radar cross-section by absorbing or scattering electromagnetic waves. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Blue Sparrow is one of a series of three of air-launched missiles originally designed by Rafael as targets to test ballistic missile defence systems. Blue Sparrow missiles can be fitted with either inert or high explosive (HE) warheads. The recovery of Sparrow-series boosters following a reported Israeli strike on an Iranian air-defence system could suggest that a derivative variant of the Blue Sparrow missile was further developed for engaging surface targets. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M824 60 mm mortar projectile dispenses a parachute-retarded illumination flare which burns for 35 seconds. The tail portion of the munition (seen here) separates from the forward (body) portion and is sometimes found along the line of fire. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Markings on this 106 mm recoilless gun projectile indicate it is a M344A1 high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) round (“CH-106-M344-A1”) produced by Fábrica Nacional de Granada (“FNG”), Spain, in 1984 (“84”). The packing crate identifies the intended weapon as an M40A1 Cañón sin retroceso, or ‘recoilless rifle’ (“C.S.R. 106 M40 A1”). Other markings show that the round is fitted with an M509-type point-impact, base initiating (PIBD) fuze (“Espoleta PIBD M509”), and give additional details such as the expected muzzle velocity (“V₀”) of 503 m/s. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the nosecone from an Israeli Tamir surface-to-air missile. This component is often found as a remnant after the functioning of the missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The AGM-179 Joint Air-to-Ground Missile (JAGM) is derived from the AGM-114 Hellfire series of air-to-surface missiles—and thus shares physical characteristics in terms of general construction, including rear fin placement. The marked weight of 52.0 kg (115 lbs) is generally believed to be an indicator that the rocket motor is from a JAGM; however, remnants marked with this weight have been observed from several years before the JAGM was initially fielded. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, four AGM-114 Hellfire-series missiles can be seen fitted to an M299-series missile launcher, itself attached to the stub wings of this Israeli AH-64 Apache helicopter. In theory, the Apache could be armed with up to sixteen Hellfire missiles, but fewer are carried in practice to allow for other weapons and sensor payloads (ARES).
Analyst Note:
In this image, two GBU-39 Small Diameter Bombs are attached to a BRU-61/A bomb rack. The Ukrainian Air Force adapted this American-designed bomb rack to fit their Soviet-designed Mikoyan MiG-29 fighter aircraft. The BRU-61/A can carry up to four GBU-39 air-delivered bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This is an Israeli 120 mm tank gun round, of the ‘armour-piercing, fin-stabilised discarding sabot – tracer’ (APFSDS-T) type. The physical features identify it as either the M322 or M338.
The projectile (penetrator) of this round has no explosive content and relies on kinetic energy to penetrate armoured targets. When a projectile is of a smaller calibre than the gun’s bore, a sabot is sometimes used to ensure the projectile is centred in the bore and to trap the gas from the propellant of the cartridge and propel the projectile. In flight, the sabot separates into two or more pieces, sometimes called ‘petals’, often found along the line of fire before the impact point. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Some tank gun projectiles may have fins affixed to an extended ‘tail boom’, in a similar manner to a mortar projectile. Note, however, that the cylindrical tail assembly is not perforated as it would be for most mortar projectiles. Tank gun projectiles are also more likely to be generally cylindrical, rather than lachrymiform (teardrop-shaped). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a component believed to be part of the folding-blade assembly used in the AGM-114R-9X variant of the Hellfire missile. Blades are used in place of an explosive payload to create a kinetic weapon that achieves a practical level of lethality whilst minimising collateral harm. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Little is known with certainty about the AGM-114-R9X variant of the Hellfire missile, although it has been associated with high-profile targeted killings including those of senior al-Qaeda figures. The weapon functions as a kinetic-impact munition, using pop-out blades—rather than an explosive warhead—to reduce the prospects of collateral harm. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
107mm spin-stabilized rockets of this design are often utilized by non-state actors in an indirect fire role. Like the original Chinese models that they are copied from, they do not require more than a simple electric power source and a rudimentary launch platform to achieve an acceptable level of accuracy. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 57E6 series of missiles fired from the 96K6 Pantsir system use a two-stage design that is unusual for surface-to-air missiles of this type. The remnant seen in this image is part of the missile’s booster section, which accelerates the second stage to a high velocity before separating. The booster section uses a distinctive toffee-brown, filament-wound composite body. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
As a result of the rapid introduction of new models and variants during ongoing conflicts, sometimes a munition is issued with a provisional designation, or with no designation at all. In other cases, the designation is not yet known to researchers. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Next-generation Light Anti-tank Weapon (NLAW) uses an uncommon form of guidance known as predicted line-of-sight (PLOS). PLOS guidance calculates the anticipated position of a moving target prior to launch, with the munition using inertial guidance to fly to the projected impact point. This fire-and-forget technique allows the operator to move positions immediately after firing, and is generally cheaper than other fire-and-forget guidance types. (ARES)