201 results
Analyst Note:
This sheet-metal body component is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR-59518”) which indicates it was produced by GlenDee Corp. of Moorpark, California, which does business as Metalagraphics, Inc. (MGI). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Moog Inc.—headquartered in East Aurora, New York, as marked on this munitions remnant—describes itself as a “worldwide designer, manufacturer, and integrator of precision control components and systems”. Moog supplies actuator and control components to the prime contractor on the Miniature Air-Launched Decoy (MALD) programme, Raytheon. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Positive identification of this surface-to-air missile cannot be made based on the imagery in the source. The items highlighted in this image are most likely the remains of either a 9M38- or 9M317-series missile, based on fin construction and their size relative to the individual posing in the foreground. These two missiles are close in design and function, and are predominantly fired from the Buk series of SAM systems. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a ‘120mm TB’ air-delivered bomb that has been adapted from a 120 mm mortar projectile. It is claimed by the manufacturer that this thermobaric munition offers improved fragmentation and blast effects when compared with standard (high explosive) 120 mm mortar projectiles. The “with special FUZE” marking refers to the use of the UT M18 impact fuze. Note that this munition cannot be fired from a mortar, despite the munition body showing features consistent with this use (e.g., gas-check bands). Instead of a standard mortar projectile tailboom which would contain an ignition cartridge and be perforated by flash holes, this munition is fitted with a simplified, plastic tailfin assembly that is designed to stabilise the munition as it falls after being released by a UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Although the source claims that this image shows a Buk-M3 surface-to-air missile system, this imagery is not sufficient to determine whether the remnants highlighted are from a 9M38-or 9M317-series guided missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this case, the tentative identification of this munition is possible based on an analysis of its silhouette, particularly the distinctive detachable warhead compartment that can be seen hanging from the base of the munition's body. In many cases, such an identification technique would not be possible to apply with confidence. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This munition remnant is marked with a manufacturer’s CAGE Code (“MFR CAGE CODE: 62313”) which indicates it was produced by Lockheed Martin. Lockheed Martin is the primary contractor that makes GMLRS missiles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This remnant shows a munition component marked with the CAGE Code for a sub-contractor who produced part of a larger munition. “64344” is the code for Unique Electronics Inc., a known sub-contractor working on Lockheed Martin’s GMLRS contract. One of the parts they make is the “CABLE ASSEMBLY W459“, as seen in this image. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Russian spherical submunition of unknown designation. Whilst this specific example was delivered by a cluster munition variant of the Kh-59MK2 missile, this submunition is known to also be delivered by variants of the Kh-69. A similar, but different, spherical submunition is delivered by some variants of the Kh-101. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows part of a Russian Kh-59MK2 missile that is fitted with a cluster munition warhead. Some of the grey spherical submunitions are visible, both inside and outside the warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Commercial and Government Entity (CAGE) code marked on this data plate (“0S9G9”) is a now-obsolete code assigned to Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), the manufacturer of the Mikholit air-delivered bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two Mikholit air-delivered bombs (‘glide bombs’), and four Mikholit warheads. There are at least two different variants of warheads available for the Mikholit glide bomb. The green cylinder on the left is a blast (high explosive) warhead, whilst the other three warheads are shaped charge warheads which incorporate additional fragmentation. Blast warheads of this type have also been seen with red markings, while the shaped charge warheads have been seen with yellow markings. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two MAM-L guided air-delivered bombs affixed to the wing of a Bayraktar TB2 drone. The MAM-L and TB2 are both produced in Türkiye by Roketsan and Baykar respectively. The MAM-L can have one of three different warheads: blast fragmentation, anti-tank, or thermobaric. The warhead section of each MAM-L in this image has “YIPE/BF” visible. ‘YIPE’ is the abbreviation of the warhead type in Turkish: Yüksek Infilaklı Parçacık Etkili (‘high explosive fragmentation’, in English). The ‘BF’ also indicates that these MAM-L munitions are of the blast-fragmentation variant. The warhead of a MAM-L cannot be determined from an external assessment without viewing markings such as these (or a clear view of the data plate, which can be seen on the aft portion of the MAM-L). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
These images show a damaged Serat-01 engine which powers the Shahed-131 drone after its rocket-assisted launch. The Serat-01 is a copy of the MDR 208 engine, and is noticeably smaller than the MD550 which powers the larger Shahed-136. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the BSF-50, one of several warheads developed by Russia for the Shahed-136/Geran-2 to replace the original Shahed-136 warhead designed by Iran. The BSF-50 is a high explosive warhead with a fragmentation effect. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the functioned rocket motor of an Israeli Carpet rocket. The Carpet uses a fuel-air explosive (FAE) warhead which is designed to function mines and improvised explosive devices (IEDs), clearing a target area for the advance of friendly forces. These rockets are fired from the Carpet rocket launcher, which is loaded with up to 20 rockets and can be fitted to a variety of vehicles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows three North Korean 120 mm high explosive (HE) mortar projectiles. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
Whilst relatively little is known about Burmese air-delivered bombs from publicly available sources, researchers (including those at ARES and Myanmar Witness) have been collecting evidence based on munitions’ physical features and markings. Combined with information from confidential sources, this has allowed for the tentative identification of several models. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This F-16I fighter aircraft from 107 Squadron Israeli Air Force is carrying a CATM-120 inert missile simulant (indicated). These devices are used for training purposes, being designed to replicate the weight and centre of gravity of a live munition. They lack any means of propulsion and are not released from the aircraft. The CATM-120 can be differentiated from the AIM-120 missile series by the presence of only blue bands on the missile, denoting both an inert rocket motor and an inert payload. A ‘live’ AIM-120 will have two brown bands on the rear section of the missile (the rocket motor), and a yellow band on the forward, or warhead, section. An AIM-120 with an inert warhead, but a live rocket motor, will have a blue band on the warhead and two brown bands on the rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The munition indicated in this image as a 152 mm high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectile manufactured in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The internal components of large, complex munitions often feature markings to aid in assembly, supply chain oversight, and quality assurance. In this case, a data plate marked with the name of the manufacturer (“MBDA FRANCE”) has been affixed to one of the rear control fins (“EQ, VENTRAL, FIN TIP”) of the missile. The NATO Stock Number (NSN) is also visible. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an actuator from a Storm Shadow-series missile. Actuators are components of guided munitions that are most often used to move control surfaces (e.g., fins and wings), enabling the munition to adjust its course in-flight in response to guidance commands. In this case, the component is fitted with a ‘data plate’ that indicates it was manufactured by MBDA France. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Microturbo TRI 60-30 turbojet engine from a Storm Shadow-series air-launched cruise missile. Further remnants of the rear of the missile are also visible, including one of the rear control fins. The Storm Shadow has a range of more than 250 kilometres. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rear of the second stage of the penetrator warhead (also called a ‘follow-through’ warhead) of the Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead system present in the Storm Shadow/SCALP-EG missile. The cylindrical object in the centre of the warhead (with a data plate marked “THALES”) is the fuze. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the first stage of the Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead used by the Storm Shadow/SCALP-EG missile. The BROACH uses a shaped-charge warhead (seen here) as its first stage, to help penetrate hardened targets, whilst the second stage comprises a conventional high explosive penetrator warhead (also called a ‘follow-through’ warhead) (ARES).
Analyst Note:
The remnant at left in this image is the second stage, or penetrator warhead, of the Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead as used in the Storm Shadow/SCALP-EG air-launched cruise missile. In this case, it has failed to function as intended. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Two of the distinctive, black tailfins used on S8-series air-to-surface rockets are visible to front and left of the remnant material. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This remnant of an MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) surface-to-surface ballistic missile is marked to indicate it is the MGM-140A variant, a cluster munition which carries 950 M74 multi-purpose submunitions. Submunitions of this type are sometimes referred to by the acronym ‘anti-personnel and anti‑materiel (APAM)’. Additional markings indicate a manufacturing date (“10/96”; October 1996), a serial number (“411240”), and other information. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The circles in this image indicate where the fixed fin assembly is connected to the bomb body. Fin assemblies such as this help stabilise the bomb as it falls, improving the predictability of the trajectory and thus precision. Fins also orient the bomb as it falls so that munition travels nose-down. Orientation of the bomb on impact can play a role in fuze functioning, as well as the distribution of explosive or other effects. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This M107 high explosive (HE) artillery gun projectile is fitted with an RT180 multi-function fuze. The RT180 can be set to operate in point-detonating or proximity modes. The factory setting for the proximity fuze detonates the warheads an average of 9 metres above the target. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
The JDAM-ER in this photograph is affixed to an unusual pylon thought to be of Ukrainian design, which allows the Western munition to be carried by the Soviet-designed Mikoyan MiG-29 and Sukhoi Su-27 fighter aircraft in service with the Ukrainian Air Force (a MiG-29 is pictured here). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M117 series of air-delivered bombs were historically referred to as ‘demolition bombs’, due to the more substantial blast effect they offer in comparison with so-called ‘general-purpose bombs’. This is achieved through the use of more energetic explosive compositions, such as Tritonal or Minol, which incorporate an oxidiser (typically aluminium powder). Today, munitions using such compositions are sometimes considered in the loose category of ‘enhanced blast munitions’, but the distinction between demolition and general-purpose bombs has largely disappeared. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The crude launch arrangement depicted in this photograph shows the ease with which many simple rocket designs can be launched. Weapons such as this are used where precision fire is not a requirement; i.e., where the target might be a whole compound, neighbourhood, or settlement, rather than a specific building or vehicle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The AGM-179 Joint Air-to-Ground Missile (JAGM) is derived from the AGM-114 Hellfire series of air-to-surface missiles—and thus shares physical characteristics in terms of general construction, including rear fin placement. The marked weight of 52.0 kg (115 lbs) is generally believed to be an indicator that the rocket motor is from a JAGM; however, remnants marked with this weight have been observed from several years before the JAGM was initially fielded. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, four AGM-114 Hellfire-series missiles can be seen fitted to an M299-series missile launcher, itself attached to the stub wings of this Israeli AH-64 Apache helicopter. In theory, the Apache could be armed with up to sixteen Hellfire missiles, but fewer are carried in practice to allow for other weapons and sensor payloads (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This is an Israeli 120 mm tank gun round, of the ‘armour-piercing, fin-stabilised discarding sabot – tracer’ (APFSDS-T) type. The physical features identify it as either the M322 or M338.
The projectile (penetrator) of this round has no explosive content and relies on kinetic energy to penetrate armoured targets. When a projectile is of a smaller calibre than the gun’s bore, a sabot is sometimes used to ensure the projectile is centred in the bore and to trap the gas from the propellant of the cartridge and propel the projectile. In flight, the sabot separates into two or more pieces, sometimes called ‘petals’, often found along the line of fire before the impact point. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Some tank gun projectiles may have fins affixed to an extended ‘tail boom’, in a similar manner to a mortar projectile. Note, however, that the cylindrical tail assembly is not perforated as it would be for most mortar projectiles. Tank gun projectiles are also more likely to be generally cylindrical, rather than lachrymiform (teardrop-shaped). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a distinctively shaped component of MBDA’s ‘Diamond Back’ joined tandem wing assembly as fitted to the GBU-39 Small Diameter Bomb (SDB). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Israeli illumination munitions—often finished in a distinctive yellow—are sometimes mistaken for high explosive munitions by observers more familiar with the NATO or U.S. marking systems. This image shows an M485-pattern illumination projectile, a base-eject type that uses a parachute-retarded canister containing a powerful candle to illuminate the battlefield.
Analyst Note:
The M825A1 155 mm smoke projectile makes use of white phosphorus (WP) to generate a brilliant white smoke. Whilst WP does have incendiary effects, the method of dispersal in the case of the M825A1 is optimised for screening and marking purposes. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image depicts either a 9M27K or 9M27K1 cargo rocket (cluster munition). The 9M27K carries the 9N210 high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) submunition, whilst the 9M27K1 carries the 9N235 HE-FRAG submunition (ARES).
Analyst Note:
Contextual information suggests that this is likely a 9M22S unguided incendiary rocket (see External Research section), but this cannot be confirmed on the basis of this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Some artillery projectiles, such as this M150 type, use a hexachloroethane-based composition (HC) to generate smoke for screening or marking purposes. In many armed forces, HC smoke munitions have partially replaced those relying on white phosphorus for similar effects. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
107mm spin-stabilized rockets of this design are often utilized by non-state actors in an indirect fire role. Like the original Chinese models that they are copied from, they do not require more than a simple electric power source and a rudimentary launch platform to achieve an acceptable level of accuracy. (ARES)

Collection
Ukraine 2022 – 2026
On 24 February 2022, Russia launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, with forces seeking to capture most major cities – including the capital Kyiv. This marked the largest conflict in Europe since the Second World War, and around a quarter of Ukrainian territory fell under Russian control – though its forces were repelled from Kyiv. […]

Collection
Israel and Gaza 2023 – 2025
On 7 October 2023, Hamas militants breached the heavily-fortified border separating Israel and the Gaza Strip, attacking numerous towns and villages. More than 1,000 people in Israel were reported killed, with more than 250 taken hostage and moved to Gaza. In response, Israel has launched one of its largest military operations of recent decades, seeking […]
Analyst Note:
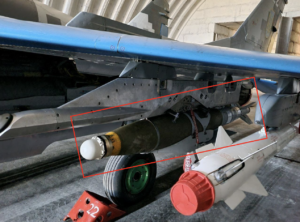
Many guided (or otherwise complex) munitions like this one are marked with additional information on individual assemblies or components. This can include information on sub-contractors that produced or integrated specific parts of a munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The MK 84 series of unguided air-delivered bombs can be converted to precision guided munitions by being fitted with guidance kits such as the Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM), SPICE 2000, or Paveway series. This MK 84 is also marked with a variant designation “MOD 4”. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The image is of "a high-velocity shell fired from the main armament of a battle tank," Desmond Travers, former director of the Institute for International Criminal Investigations, told Airwars and AFP. "The calibre appears to be 120 mm, and the shell is fin-stabilised. The maximum effective range is five kilometers, but a skilled tank crew member should be able to hit a target the size of a car." (Airwars)
Analyst Note:
122 mm ‘Grad’ rockets can be fired from a variety of launchers and even in improvised ways. The most common is the BM-21 launcher and its later derivatives, but many other portable or vehicle-mounted launchers have been used around the world. Craft-produced examples—ranging from simple rails to more complex designs comparable to factory made launchers—are also common. In some cases, Grad rockets are even fired whilst supported by a crude arrangement of logs, bricks, or rocks. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Next-generation Light Anti-tank Weapon (NLAW) uses an uncommon form of guidance known as predicted line-of-sight (PLOS). PLOS guidance calculates the anticipated position of a moving target prior to launch, with the munition using inertial guidance to fly to the projected impact point. This fire-and-forget technique allows the operator to move positions immediately after firing, and is generally cheaper than other fire-and-forget guidance types. (ARES)