404 results
Current Filter
Hinged/Actuated Fins
Fins that can be adjusted during flight to allow the alteration of a munition’s trajectory, or those that can be adjusted to reduce the size of a munition during transport and employment.
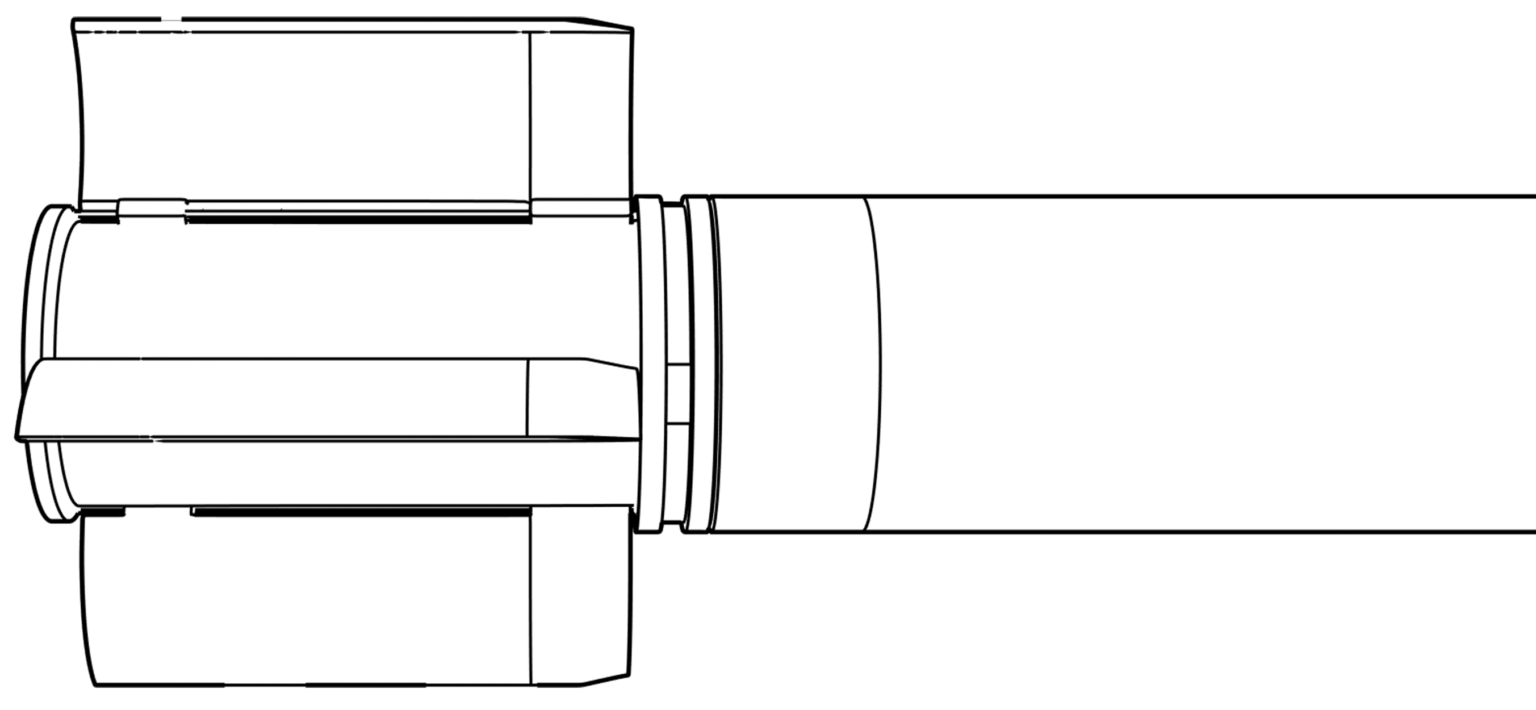
Analyst Note:
The UMPK guidance package is a ‘bolt-on’ kit that can be fitted to unguided air-delivered bombs to convert them to guided munitions. The UMPK kit also greatly extends the range of the munition to which it is fitted, allowing aircraft to strike from beyond the range of many air-defence systems. Currently only Russia manufacturers and uses these kits. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an FN-6-series man-portable air-defence system (MANPADS) being fired. In Sudan, this weapon is referred to as the ‘Nayzak’. The Nayzak is most likely a Chinese FN-6 re-marked for domestic use. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a russian air-delivered bomb fitted with a UMPK guidance kit. Not enough of the bomb is visible to positively identify the model, but it is most likely an OFAB-250-270 based on what can be seen of the tail section. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image appears to show a remnant from either a 9M38- or 9M317-series surface-to-air missile. Positive identification of this munition cannot be made based on the imagery in this source alone; a rear control fin is visible in image but the 9M38- and 9M317-series missiles use indistinguishable rear fins. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) is a guided air-delivered ‘glide bomb’ that allows for long-range strikes using an unpowered munition. The AGM-154C and AGM-154C-1 variants (a remnant of the latter pictured here) carry a Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead which uses a WDU-44 shaped-charge warhead as its first stage, to help penetrate hardened targets, whilst the WDU-45 second stage comprises a conventional high explosive penetrator warhead (also called a ‘follow-through’ warhead). The AGM-154C-1 is described by the U.S. Navy as their “first air-to-ground Network-Enabled Weapon (NEW) capable of attacking stationary land and moving maritime targets. It includes GPS/INS guidance, terminal IR seeker and a Link 16 weapon data link. Integration of the Link-16 weapon data link and updated seeker software algorithms provide a capability against at-sea moving/relocatable targets.” (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mk 104 Dual Thrust Rocket Motor (DTRM), the second-stage rocket motor for the SM-2, SM-3 Blk I, and SM-6 missiles. Based on the strakes or fins attached to this Mk 104, it can be determined that it was part of an SM-3 Blk I series missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Markings on the forward section of this small, air-delivered bomb suggest that the designation is ‘BK-3OF’ (“БК-3ОФ”). The physical features of the munition suggest that it is laser-guided and likely carries a high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) payload. This image shows the only known example, which was allegedly captured by Russian forces in conjunction with a Ukrainian UAV. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Russian air-delivered cluster bomb is marked with a threatening message directed at the French people: «Français! Changer la politique du président dans le pays, sinon ces bombes vont changer le lieu d'atterrissage!» (“French people! Change the president’s policy in the country, otherwise these bombs will change their landing site!”). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Positive identification of this surface-to-air missile cannot be made based on the imagery in the source. The items highlighted in this image are most likely the remains of either a 9M38- or 9M317-series missile, based on fin construction and their size relative to the individual posing in the foreground. These two missiles are close in design and function, and are predominantly fired from the Buk series of SAM systems. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Although the source claims that this image shows a Buk-M3 surface-to-air missile system, this imagery is not sufficient to determine whether the remnants highlighted are from a 9M38-or 9M317-series guided missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image represents the first documented instance of a Shahed-series UAV carrying an R-60 air-to-air missile. This appears to add a new capability to the Shahed, enabling it to target enemy aircraft. Arming UAVs to counter interception and engage alternative targets is an emergent trend. Previously, unmanned surface vessels (USVs) employed by the Ukrainian Armed Forces have been observed carrying R-73 air-to-air missiles, for example. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rear section of a Hydra-70 rocket. The Hydra-70 uses the MK 66 series of rocket motors, visible here, but can be fitted with at least 11 different warheads. They can also be fitted with the Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS) ‘bolt-on’ guidance kit, converting an unguided rocket into a guided missile. From the available imagery, it is not clear with which warhead or guidance section this munition may have been fitted. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the venturi and tailfin assembly from a 57 mm S-5 series rocket. The S-5 series of rockets are commonly used around the world in a variety of roles, including air-to-surface and surface-to-surface. Unfortunately, from this image alone the specific model and country of origin cannot be determined. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
A Gerbera-series UAV is pictured here being carried by just two Ukrainian soldiers. This highlights the Gerbera’s lightweight design—the airframe is mostly constructed from Styrofoam and wood, which saves on both weight and cost. This particular example does not bear signs of significant damage, suggesting that it either malfunctioned or was brought down by EW and crashed. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows parts from at least three fin-stabilised tank gun projectiles, including the tail assemblies and several folding fins. These are components that often survive relatively intact following the functioning of such munitions. The specific morphology of the remnants pictured is consistent with Israeli 120 mm tank gun projectiles. Contextual information suggests that the remnants are most likely to be from M339 high explosive ‘multi-purpose’ projectiles. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of a control fin from a Paveway III bomb guidance kit that is compatible with 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bombs. In U.S. service, this combination receives designations in the GBU-24 series. Based off this remnant alone, it cannot be determined which model of air-delivered bomb was paired with this particular guidance kit. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a GBU-12 series guided bomb being loaded onto a F-35B belonging to Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 211. Two of the control fins have not yet been installed in the Paveway’s guidance control section. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the control fin of a GBU-24 (as seen partially marked), the designation for the combination of a Paveway III guidance kit paired with a 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bomb. This remnant is not enough to determine which model of bomb the kit was originally paired with. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a BLU-111 500-pound-class bomb paired with a Paveway II guidance kit, and an MXU-650 series airfoil group, or tail kit. This combination is designated the GBU-12 series in U.S. service. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows various remnants of an air-delivered bomb and a Paveway guidance kit. The blue pen provides a scale indicator, which is necessary to identify which variant of aerofoil (‘airfoil’) group the tail fins belonged to. In this case, they are most likely from an MXU-650-series airfoil group, which are paired with MK-82 500-pound-class bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This still taken from a video released by Iranian state media, shows a one-way-attack UAV purportedly manufactured by Israeli forces operating inside Iran. This UAV was found alongside manufacturing equipment, and additional UAV components, strongly suggesting that it was manufactured or assembled inside Iranian borders. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the guidance control unit from a Paveway- or Lizard-series bomb guidance kit. The guidance control fins are marked “FOR USE ON MK82” indicating that this guidance control unit was paired with a MK 82-series 500-pound-class bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a variety of remnants from an Israeli SPICE 250 guided bomb. One of the bomb’s four control fins is visible at the bottom-left of the image. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a remnant of the control section of the Arrow 2 ‘kill vehicle’, including the control fins. The blast-fragmentation warhead is located in the front section of the kill vehicle, forward of the control section, and is absent here due to the functioned state of the munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mikholit that was ejected from the weapons pod of an Israeli Hermes 900 drone that was downed in Iran. This Hermes 900 drone had two weapons pod, each capable of carrying 4 Mikholit bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The source for this entry reports that these remnants were left behind after the missiles were “recycled“. Explosive remnants of war (ERW) are often recycled for the value of their scrap metal, or ‘harvested’ by militant groups for the explosive material. These recycling attempts may result in the ERW exploding, potentially killing or injuring people. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the guidance control unit from an Israeli 'Chameleon 3’ bomb guidance kit. This kit appears similar to those in the Israeli Lizard series of guidance kits, which are derived from the American-designed Paveway kit series. (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows the damaged aerofoil group, or ‘tail kit’, found with a Chameleon 3 bomb guidance kit. The exact model of aerofoil group is unknown, but in US service similar component groups are given a designation in the ‘MXU-xxx’ range, and are interchangeable with different variants of the Paveway bomb guidance kit (within bomb weight classes). (ARES).
Analyst Note:
Although Human Rights Watch reported that they found manufacturing markings on a guidance fin assembly indicating that this MXU-series aerofoil group was paired with a Paveway III guidance kit, this cannot be determined by this wing remnant from the aerofoil group alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the remnants of a SkyStriker one-way attack UAV, manufactured by Elbit Systems of Israel. The SkyStriker can be fitted with various warhead options, including dual-purpose warheads weighing 5 or 10 kilograms. While it appears that a reconstruction was attempted with the remnants, the placement of the various components does not accurately represent an intact SkyStriker. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the flare from a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system's ‘Talon’ kinetic interceptor missile. The flare is located at the aft end of the missile's booster engine. The ‘petals’ of the flare are initially flush, and are actuated into the deployed position, seen here, as part of the missile‘s functioning. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mikholit glide bomb, with its warhead removed (green cylinder on the left side of the box). The fins that spring outward when deploye have been taped down. This Mikholit was reportedly recovered by the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) from Hamas, who had captured the bomb after it failed to function when originally deployed by the IDF. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows two Mikholit air-delivered bombs (‘glide bombs’), and four Mikholit warheads. There are at least two different variants of warheads available for the Mikholit glide bomb. The green cylinder on the left is a blast (high explosive) warhead, whilst the other three warheads are shaped charge warheads which incorporate additional fragmentation. Blast warheads of this type have also been seen with red markings, while the shaped charge warheads have been seen with yellow markings. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows various remnants from GBU-39 air-delivered bombs, including two fuze wells. Each GBU-39 has only a single fuze well, indicating that this picture shows the remnants of at least two different GBU-39 bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image and the related entries show fragments of an AGM-84 Standoff Land Attack Missile-Expanded Response (SLAM-ER) series missile. AGM-84 SLAM-ER missiles are AGM-84E Standoff Land Attack Missiles (SLAM) that incorporate certain upgrades, including wings to increase the missile's range. The AGM-84 series include the anti-ship ‘Harpoon’ variants, from which the SLAM and SLAM-ER series are derived. As a result, many remnants will be similar or identical between variants. The wing remnant here is diagnostic, however. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows several GBU-53/B bombs photographed from above while on a munitions transport cart. GBU-53/B bombs are transported and loaded onto the aircraft with the wing assembly on the bottom. When the GBU-53/B is released from the aircraft, the bomb rotates, with the wing assembly side orienting as the top as the bomb glides to its target. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows several remnants of a MAM-L bomb that are typically found after functioning. The actuated fins, as well as the fixed fins, are visible, along with various components of the control section that actuate the fins. The actuated fins attach to the control section, at the rear of the bomb, while the fixed fins attach to the middle of the bomb body. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an American F/A-18 fighter aircraft armed with two AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) air-delivered bombs taking off to conduct strikes against Houthi forces in Yemen. The F/A-18 likely has two more AGM-154-series munitions carried on the opposite side of the aircraft, for a total of four bombs. The JSOW has multiple variants which are fitted with different warheads, including a submunition payload (AGM-154A and AGM-154B models), BLU-111 500-pound bomb (AGM-154A-1), and a Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage penetrator warhead (AGM-154C or AGM-154C-1). All variants are externally identical without markings, with the exception that the AGM-154C and C-1 have a small reflective window on the bottom of the nose for the terminal infrared (IR) seeker. The munitions in the image are most likely AGM-154A-1 or AGM-154C-series bombs, due to the lack of reported submunitions following the strikes. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a relatively intact Shahed-131 one-way-attack (OWA) UAV with various components highlighted, including the GPS antenna array (light blue), fuselage (light purple), engine (yellow), wing stabiliser (orange), and nose cone (cyan, inside the red box). The nose cone attaches to the front of the fuselage and covers the warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Two R-77 air-to-air missiles (NATO reporting name: AA-12 Adder) are carried in this photograph by a Russian Aerospace Forces Sukhoi Su-35 fighter aircraft. Key markings, including the aircraft’s bort number (a coloured numeral that acts as a unit or base identifier), have been digitally obscured. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Armement Air-Sol Modulaire (AASM; ‘Modular Air-to-Ground Armament’) family of French bolt-on guidance kits are fitted to air-delivered bombs of various sizes in a similar fashion to American JDAM kits. In some marketing materials, the acronym HAMMER is used, standing for ‘Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range’. This refers, in part, to the rocket boosters fitted to munitions in the family to extend their effective range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this photo, a Ukrainian Sukhoi Su-25 ground-attack aircraft from the 299th Tactical Aviation Brigade, with the bort number ‘Blue 28’, is seen carrying an AASM-250 guided air-delivered bomb under its left wing. Available imagery shows that the AASM-250 has also been fitted to Mikoyan MiG-29 fighter aircraft, and can likely be carried by the Sukhoi Su-27 as well. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Israeli Air Force F-16 carrying four Rampage air-to-ground missiles. The Rampage is a 580 kg (1,278 lb) missile with GPS and INS guidance. It carries a multi-purpose warhead that is designed for engaging a range of targets in the open as well as offering some degree of penetration. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This F-16I fighter aircraft from the Israeli Air Force is carrying a CATM-120 inert missile simulant (indicated). These devices are used for training purposes, being designed to replicate the weight and centre of gravity of a live munition. They lack any means of propulsion and are not released from the aircraft. The CATM-120 can be differentiated from the AIM-120 missile series by the presence of only blue bands on the missile, denoting both an inert rocket motor and an inert payload. A ‘live’ AIM-120 will have two brown bands on the rear section of the missile (the rocket motor), and a yellow band on the forward, or warhead, section. An AIM-120 with an inert warhead, but a live rocket motor, will have a blue band on the warhead and two brown bands on the rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a wing fragment from a SPICE-1000 bomb guidance kit. While there are no remnants of the bomb body visible, it can be determined that a MK 83-series 1,000-pound bomb or similar was used, as MK-83 series bombs are paired with the SPICE-1000 bomb guidance kit to form a complete munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Whilst there are no visible markings explicitly identifying the model of the 122 mm rockets in this image, they are sitting atop a box marked “R-122” and exhibit physical features consistent with North Korean R-122 rockets. It should be noted that rockets marked with the generic “R-122” model name have been observed in both ‘long’ and ‘short’ overall lengths and painted in different colours. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This F-16I fighter aircraft from 107 Squadron Israeli Air Force is carrying a CATM-120 inert missile simulant (indicated). These devices are used for training purposes, being designed to replicate the weight and centre of gravity of a live munition. They lack any means of propulsion and are not released from the aircraft. The CATM-120 can be differentiated from the AIM-120 missile series by the presence of only blue bands on the missile, denoting both an inert rocket motor and an inert payload. A ‘live’ AIM-120 will have two brown bands on the rear section of the missile (the rocket motor), and a yellow band on the forward, or warhead, section. An AIM-120 with an inert warhead, but a live rocket motor, will have a blue band on the warhead and two brown bands on the rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Stunner surface-to-air missile fired by the David’s Sling air defence system is a two-stage interceptor, meaning that the munition contains two separate rocket motors for launch and propulsion. The first stage, or launch motor, detaches from the munition after a short time, before the second stage, or flight motor, ignites. The second stage motor, visible here, was found relatively intact. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The internal components of large, complex munitions often feature markings to aid in assembly, supply chain oversight, and quality assurance. In this case, a data plate marked with the name of the manufacturer (“MBDA FRANCE”) has been affixed to one of the rear control fins (“EQ, VENTRAL, FIN TIP”) of the missile. The NATO Stock Number (NSN) is also visible. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Microturbo TRI 60-30 turbojet engine from a Storm Shadow-series air-launched cruise missile. Further remnants of the rear of the missile are also visible, including one of the rear control fins. The Storm Shadow has a range of more than 250 kilometres. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, two GBU-39 guided air-delivered bombs can be seen in their shipping containers, with only the nose and the tail actuation section of the munitions clearly visible. Distinctive packaging such as this can sometimes be used as contextual evidence for the presence of specific munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This U.S. Department of Defense file photo shows an M142 High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) launching an MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) series tactical ballistic missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Blue Sparrow-series air-launched ballistic missile is being carried by an F-15C fighter aircraft from 106 Squadron Israeli Air Force. The missile is marked with the logos of three organisations involved in its development—the U.S. Missile Defense Agency, the Directorate of Defence Research & Development, and the Israel Missile Defense Organization—and the Blue Sparrow programme logo of the manufacturer (Rafael Advanced Defense Systems). The booster section also features bright-orange fins and markings consistent with its use as a target missile, here modified to accept a high explosive warhead. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Blue Sparrow is one of a series of three of air-launched missiles originally designed by Rafael as targets to test ballistic missile defence systems. Blue Sparrow missiles can be fitted with either inert or high explosive (HE) warheads. The recovery of Sparrow-series boosters following a reported Israeli strike on an Iranian air-defence system could suggest that a derivative variant of the Blue Sparrow missile was further developed for engaging surface targets. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M22S is essentially the ‘full-sized’ version of the shorter 9M28S surface-to-surface rocket previously recorded in the OSMP. Both rockets carry the same 9N510 incendiary warhead, but differ in the length of their rocket motor sections, and thus range. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Stunner missile is the surface-to-air interceptor missile fired by the David’s Sling weapon system to defeat short-range ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, drones, and rockets. The Stunner does not carry an explosive warhead, instead relying on kinetic impact (also called the ‘hit-to-kill’ principle) to intercept ballistic missiles and other targets. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M28S surface-to-surface unguided rocket carries the 9N510 warhead, which disperses burning thermite-type incendiary elements over a wide area upon functioning. This munition is designed to start fires in target areas vulnerable to incendiary attack, including forests, ammunition dumps, and fuel storage sites. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows most of the forward half of a Tamir surface-to-air missile, including the guidance section and warhead, as fired by launchers in the Iron Dome system. These interceptor missiles are fast and manoeuvrable with a relatively small explosive payload. Their construction and low yield means that remnants are often recovered largely intact. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The RAFAEL Advanced Defense Systems SPICE 1000 guidance kit is fitted to MK 83-series 1,000-pound unguided air-delivered bombs to convert them to precision guided munitions. Like the JDAM-ER, it has a deployable wings to provide a ‘gliding’ attack trajectory. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The BLU-117 air-delivered bomb is nearly identical in format to the more common MK 84, but uses the PBXN-109 explosive filler which is more insensitive than the typical explosive compositions found in MK 80-series bombs. The BLU-117 is also coated with a grey, thermally resistant paint, and marked with three yellow bands (as opposed to the green paint with two yellow bands found on standard MK 80-series bombs). These changes were requested by the U.S. Navy for safer storage of these munitions aboard ships. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The visible component is part of a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) guidance kit, an accessory package that is fitted to unguided air-delivered bombs to convert them to precision guided munitions. Specifically, this image shows a control fin from the tail assembly. Whilst the JDAM kit would not constitute a munition in its own right, this remnant is included in the OSMP as contextual information strongly suggests it formed part of a complete munition that functioned. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
The JDAM-ER in this photograph is affixed to an unusual pylon thought to be of Ukrainian design, which allows the Western munition to be carried by the Soviet-designed Mikoyan MiG-29 and Sukhoi Su-27 fighter aircraft in service with the Ukrainian Air Force (a MiG-29 is pictured here). (ARES)
3 Analyst Notes:
This is an image released by the Israeli Defense Forces that shows an F-15I of 69 Squadron Israeli Air Force preparing to take part in a high-profile airstrike on 27 September 2024, in which the leader of Hezbollah, Hassan Nasrallah, was killed.
Analyst Note:
The MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) series includes variants with a variety of different payloads, including submunitions and unitary high explosive (HE) warheads. The number of submunitions carried and effective ranges also vary.
Ukraine has reportedly received the MGM-140A and MGM-140B variants, which are externally visually identical and must usually be distinguished by markings. The MGM-140A carries 950 M74 submunitions, with an effective range of 165 km, while the MGM-140B carries only 300 M74 submunitions but has a longer effective range of 300 km. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The crude launch arrangement depicted in this photograph shows the ease with which many simple rocket designs can be launched. Weapons such as this are used where precision fire is not a requirement; i.e., where the target might be a whole compound, neighbourhood, or settlement, rather than a specific building or vehicle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an Israeli Air Force F-16C fighter aircraft from 101 Squadron carrying a MK 84-series 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bomb fitted with a SPICE 2000 ‘bolt-on’ guidance kit. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M14 Malyutka anti-tank guided missile was designed and fielded by the Soviet Union in the 1960s. It uses an outdated guidance principle known as manual command to line-of-sight (MCLOS), in which the operator must manually adjust the course of the missile in flight. Nonetheless, this munition has been seen in several 21st-century conflicts. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, an F-15C fighter aircraft from 106 Squadron Israeli Air Force is seen carrying two MK 84-series 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bombs fitted with Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) ‘bolt-on’ guidance kits. In U.S. service, this combination is known as the GBU-31. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Joint Direct Attack Munition – Extended Range (JDAM-ER) marries the JDAM guidance kit to a ‘glide bomb’ wing kit developed by the Australian Defence Force, offering a munition with at least three times the range of a standard GBU-38 500-pound-class guided aerial bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, two GBU-39 Small Diameter Bombs are attached to a BRU-61/A bomb rack. The Ukrainian Air Force adapted this American-designed bomb rack to fit their Soviet-designed Mikoyan MiG-29 fighter aircraft. The BRU-61/A can carry up to four GBU-39 air-delivered bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The M329 is a multi-purpose tank gun projectile designed to engage a range of targets other than tanks. It is one of the few cluster munitions that takes the form of a tank gun projectile, dispensing six explosive submunitions over a relatively small area. It has also been referred to as the ‘APAM 120’, describing its functional role (‘anti-personnel/anti-materiel’) and calibre (120 mm). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a distinctively shaped component of MBDA’s ‘Diamond Back’ joined tandem wing assembly as fitted to the GBU-39 Small Diameter Bomb (SDB). (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Contextual information suggests that this is likely a 9M22S unguided incendiary rocket (see External Research section), but this cannot be confirmed on the basis of this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The various Iranian Qaem-series guided air-delivered bombs can be difficult to differentiate from one another. In this case, the wing (forward fin) assembly distinguishes this Qaem-5 from the visually similar Qaem-1. Note also that the name 'Qaem' has applied by Iran to other, unrelated munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image features both delivered (the two left-most munitions) and undelivered munitions of the same model.
Analyst Note:
Like the more common 9M22S rocket, the 9M28S carries the 9N510 warhead, which dispenses 180 individual incendiary elements composed of a magnesium alloy shell filled with a thermite-like incendiary composition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
122 mm ‘Grad’ rockets can be fired from a variety of launchers and even in improvised ways. The most common is the BM-21 launcher and its later derivatives, but many other portable or vehicle-mounted launchers have been used around the world. Craft-produced examples—ranging from simple rails to more complex designs comparable to factory made launchers—are also common. In some cases, Grad rockets are even fired whilst supported by a crude arrangement of logs, bricks, or rocks. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Next-generation Light Anti-tank Weapon (NLAW) uses an uncommon form of guidance known as predicted line-of-sight (PLOS). PLOS guidance calculates the anticipated position of a moving target prior to launch, with the munition using inertial guidance to fly to the projected impact point. This fire-and-forget technique allows the operator to move positions immediately after firing, and is generally cheaper than other fire-and-forget guidance types. (ARES)