Featured Materials
A curated selection of images, terms and collections to help understand modern conflict.
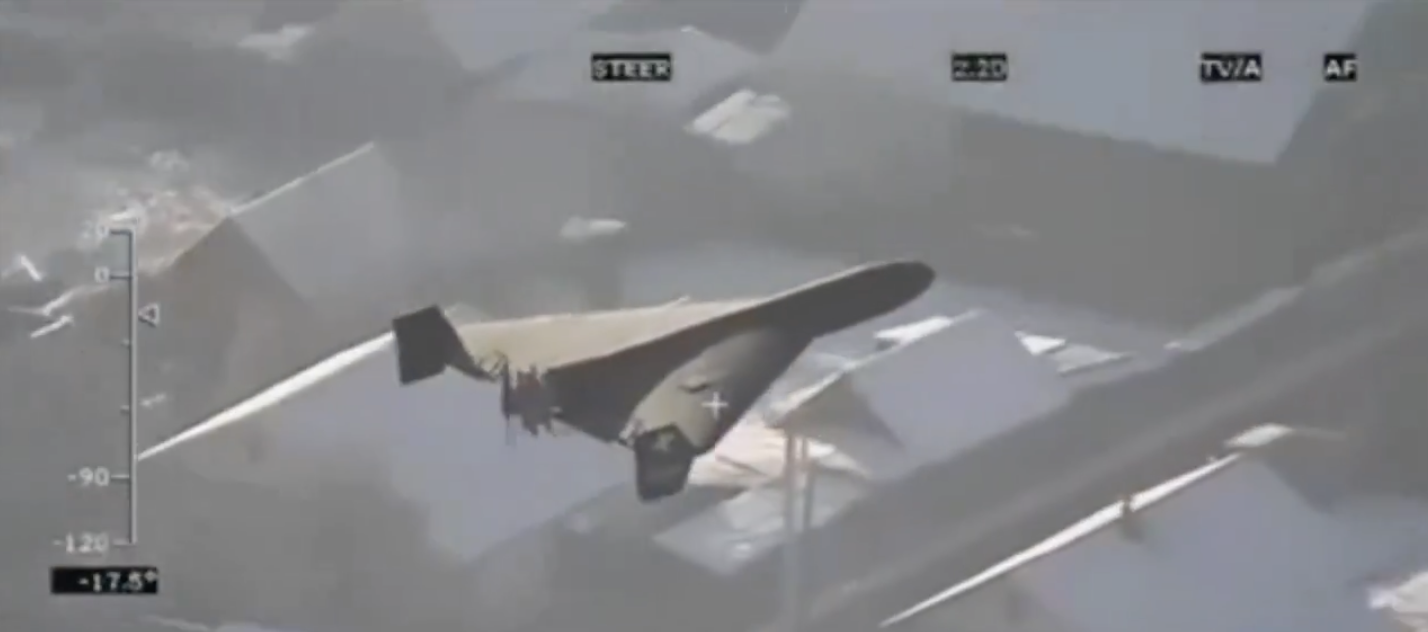

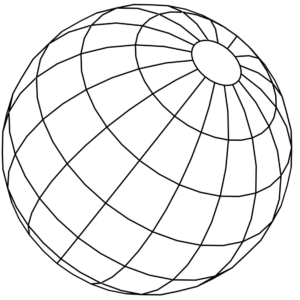
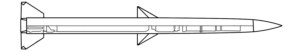
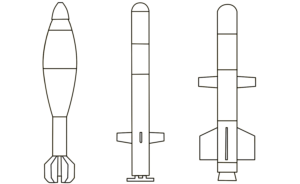
Shahed-131 & -136 UAV
3D models explain the best-known 'kamikaze drones'

Collection
Israel and Gaza 2023 – 2025
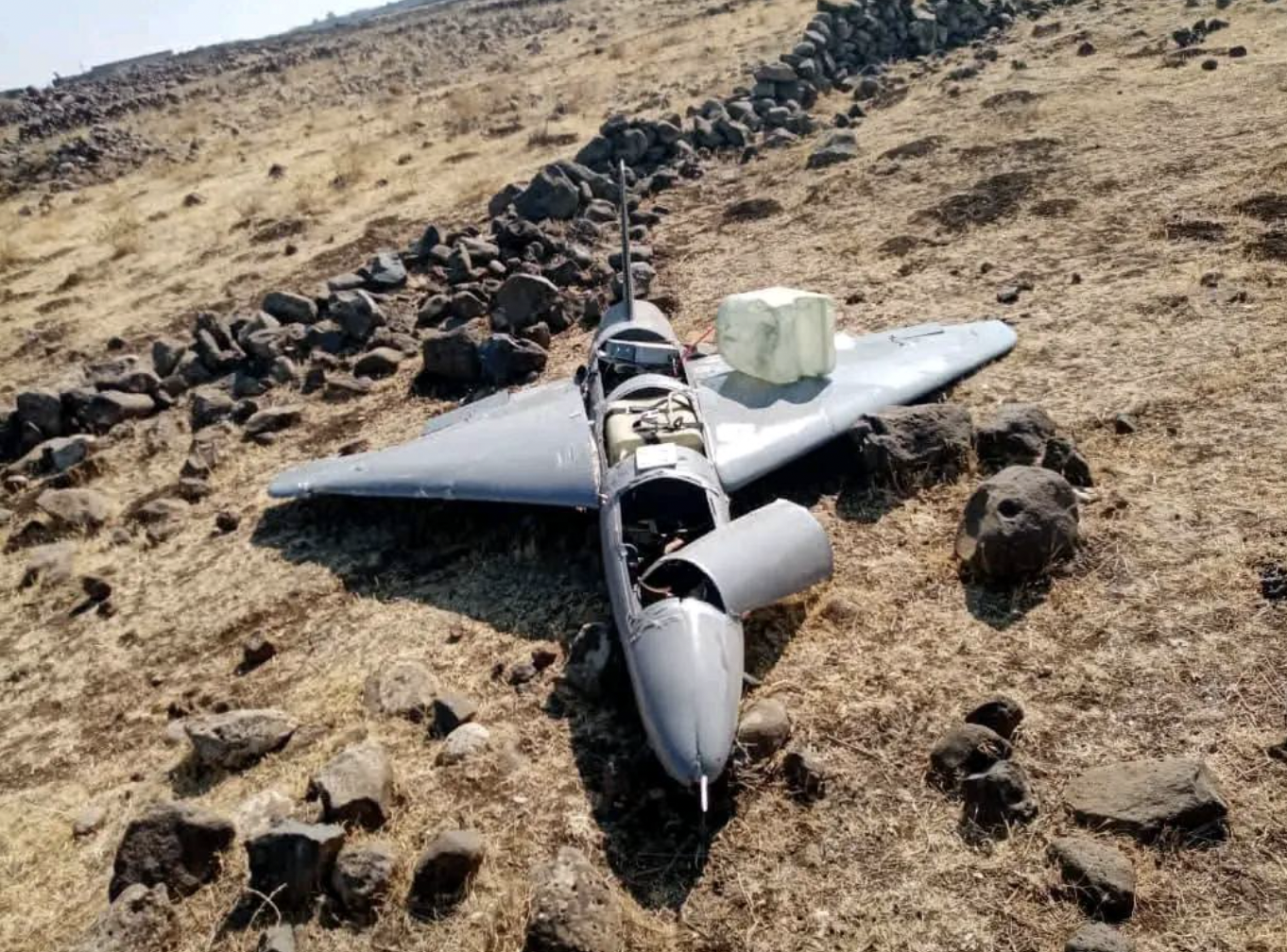

Collection
The munitions of the Iran-Israel 12-day war
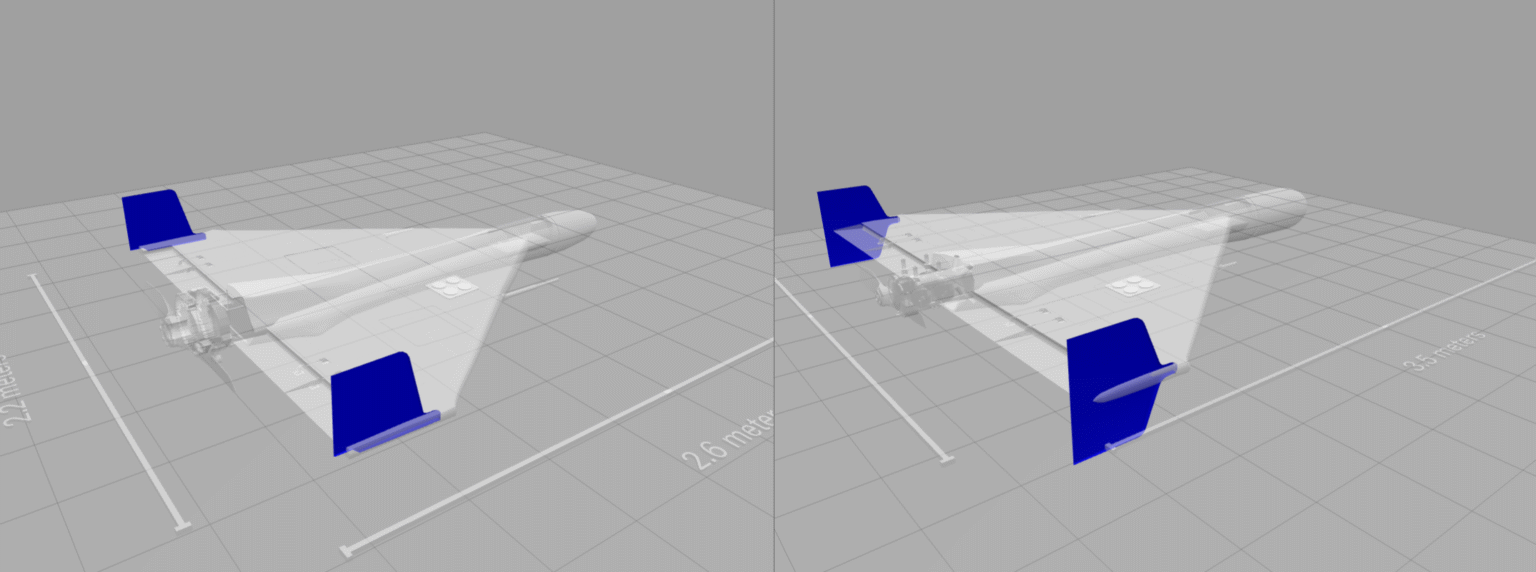
Шахед‑131 і Шахед‑136 БпЛА
Our visual guide to the Shahed in Ukrainian

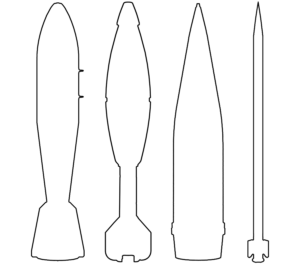
GBU-39 bomb
3D model explaining Israel's 'weapon of choice' in Gaza

Research organisation
Images from the Human Rights Watch archives

Collection
The munitions of Trump's Yemen campaign

Collection
Ukraine 2022 – 2025

Follow
Keep up to date with newly added munitions

Contribute
Submit images to the OSMP
45 results
Analyst Note:
This image shows a improvised rocket-assisted munition (IRAM). This particular munition consists of a 107 mm rocket motor with an industrial gas cylinder fitted in place of the standard warhead. The frost present on the cylinder indicates a pressurised gas was released. The yellow–green residue is consistent with a payload of chlorine gas. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows one of the two improvised air-delivered munitions (IADMs) containing a chemical payload used in an attack by the Syrian Arab Air Force on 7 April 2018 in Douma, Syria. This image shows how the IADM comprises a cradle surrounding an industrial gas cylinder. These cradles typically incorporate fins, wheels, and lifting lugs. The fins and the wheels of the cradle can be seen in this image (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a conventional 122 mm high explosive artillery projectile that has been modified to carry a chemical payload. It is one of several used in an attack by the so-called ‘Islamic State’ on the town of Marea, Syria. The black substance on the ground is suggestive of low-purity sulphur mustard, a chemical warfare agent. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an impact crater, as well as remnants of the frame or ‘cradle’ (red box) that was fitted to the gas cylinder. Cradles associated with this type of Syrian Government chemical munition typically feature fins to help orient the cylinder as it falls, and features to assist with loading the cylinders into aircraft for deployment, such as wheels and lifting lugs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an industrial gas cylinder that was reportedly dropped by a helicopter over Kafr Zeita on 1 October 2016. The gas cylinder ruptured on impact with the ground, dispersing its payload of chlorine gas. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a fragment of an Israeli 120 mm tank gun projectile, with its distinctive obturating band configuration. The additional remnants shown in the related OSMP entry permit distinguishing this projectile from other potential Israeli models, identifying it as the M339 tank gun projectile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
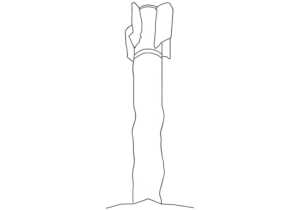
Depicted here is the MD-550 motor of a Shahed-136/Geran-2. This image was presented by Ukrainian President Zelenskyy as a fragment of the drone that reportedly hit the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant’s New Safe Confinement shelter. (ARES)
3 Analyst Notes:
This is an image released by the Israeli Defense Forces that shows an F-15I of 69 Squadron Israeli Air Force preparing to take part in a high-profile airstrike on 27 September 2024, in which the leader of Hezbollah, Hassan Nasrallah, was killed.
Analyst Note:
This is an Iranian 60 mm mortar projectile, marked to indicate it is of the ‘high explosive, long-range’ type (“H.E L.R”). Both the munition body and fuze are marked to with the year of production (“2008”). Whilst the tan colouring is often indicative of Iranian-made munitions (especially where the fins are also painted), this is not diagnostic, and a combination of physical features and markings should be assessed to reach a positive identification. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Contextual information, including an assessment of the crater which appears to be linked to this munition remnant, suggests that a 2,000-pound-class bomb fitted with a SPICE 2000 guidance kit was used in this airstrike. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Markings on this 106 mm recoilless gun projectile indicate it is a M344A1 high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) round (“CH-106-M344-A1”) produced by Fábrica Nacional de Granada (“FNG”), Spain, in 1984 (“84”). The packing crate identifies the intended weapon as an M40A1 Cañón sin retroceso, or ‘recoilless rifle’ (“C.S.R. 106 M40 A1”). Other markings show that the round is fitted with an M509-type point-impact, base initiating (PIBD) fuze (“Espoleta PIBD M509”), and give additional details such as the expected muzzle velocity (“V₀”) of 503 m/s. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Iranian M91 81 mm mortar projectile is marked to indicate it was produced in 2009. The AZ111A2 fuze fitted to the projectile is also marked with the same year of manufacture. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The 9M14 Malyutka anti-tank guided missile was designed and fielded by the Soviet Union in the 1960s. It uses an outdated guidance principle known as manual command to line-of-sight (MCLOS), in which the operator must manually adjust the course of the missile in flight. Nonetheless, this munition has been seen in several 21st-century conflicts. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
‘Khaibar-1’ is a designation given to a series of 302 mm rockets produced in Syria, possibly derived from the Chinese WS-1/WS-1B. The Khaibar-1 is also referred to as the M-302 or M302. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Iranian M48 120 mm mortar projectile is marked to indicate it was manufactured in 2008. A plastic bag cable-tied to the tail of the munition protects the auxiliary, or supplemental, propellant charges fitted to the round. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
These M485 series 155 mm artillery gun projectiles are painted yellow to indicate their functional type: illumination rounds. The M485 series of illumination projectiles are base-eject munitions that expel a parachute-retarded illuminant canister which casts light over the battlefield as it descends. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This Iranian copy of the Chinese Type 63 107 mm rocket is marked with a red stripe and text to indicate it is of the high explosive incendiary (“H.E.I”) type. Markings also show that it was produced in 2007. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The physical features, colour scheme, and packaging of these 120 mm mortar projectiles are all consistent with Iranian manufacture, but the markings are mostly obscured in this image. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Tamir Interceptor is the missile fired from Israel’s Iron Dome defence system to intercept incoming rockets, missiles, projectiles, and unmanned aerial vehicles (‘drones’). The Tamir uses a warhead with a relatively small explosive yield, which typically results in the guidance section, nosecone, and (spent) rocket motor falling to the ground relatively intact after functioning. (ARES)