Analyst Note:
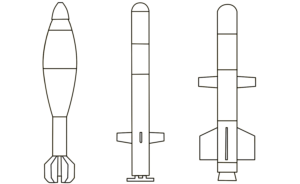
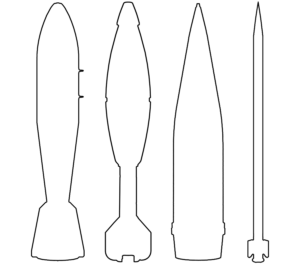
This PG-7VR recoilless gun projectile is painted in a tan colour often associated with Iranian production, but also used by other manufacturers. Iranian munitions have been seen and reported in Sudan with regularity. (ARES)

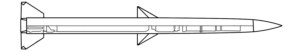
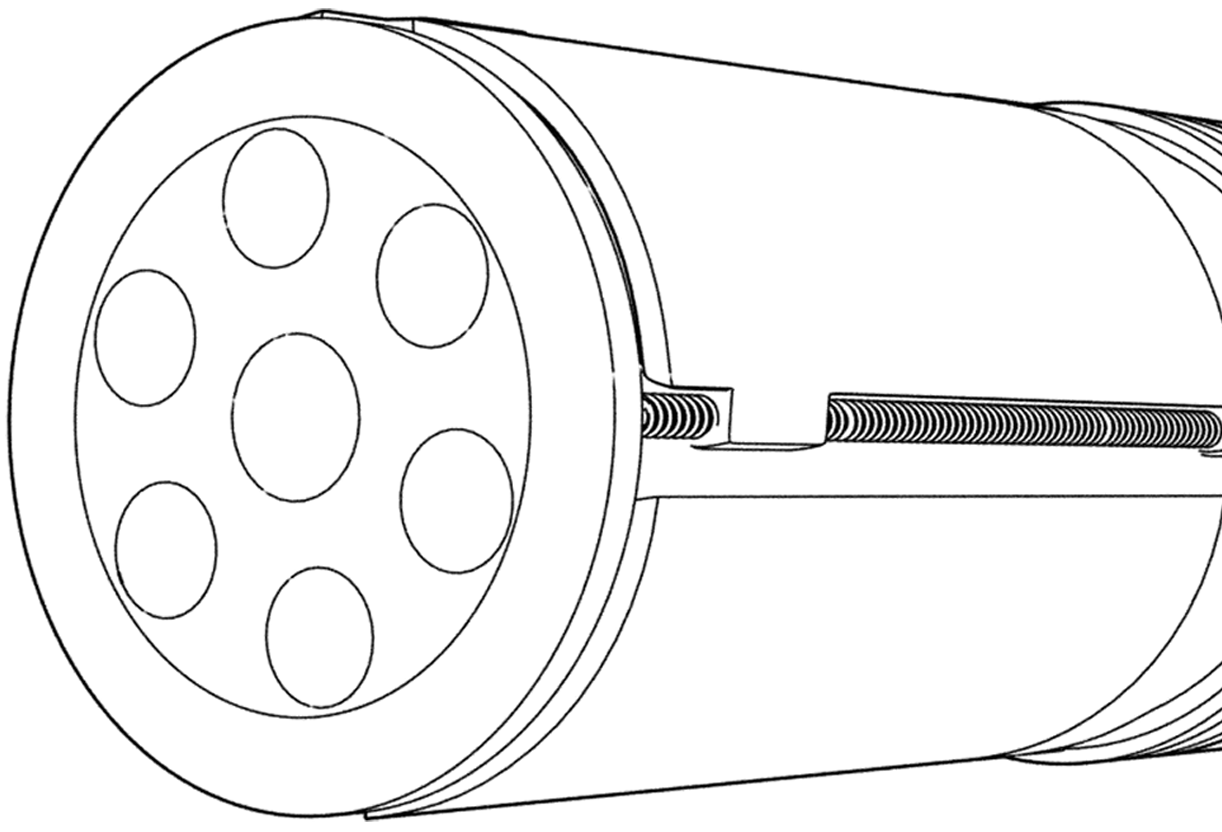 Constricting openings in rocket motors that increase the velocity and pressure of exiting gases, sometimes directing these to impart spin to the munition
Constricting openings in rocket motors that increase the velocity and pressure of exiting gases, sometimes directing these to impart spin to the munition