Analyst Note:
The AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) is a guided air-delivered ‘glide bomb’ that allows for long-range strikes using an unpowered munition. The AGM-154C and AGM-154C-1 variants (a remnant of the latter pictured here) carry a Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge (BROACH) multi-stage warhead which uses a WDU-44 shaped-charge warhead as its first stage, to help penetrate hardened targets, whilst the WDU-45 second stage comprises a conventional high explosive penetrator warhead (also called a ‘follow-through’ warhead). The AGM-154C-1 is described by the U.S. Navy as their “first air-to-ground Network-Enabled Weapon (NEW) capable of attacking stationary land and moving maritime targets. It includes GPS/INS guidance, terminal IR seeker and a Link 16 weapon data link. Integration of the Link-16 weapon data link and updated seeker software algorithms provide a capability against at-sea moving/relocatable targets.” (ARES)
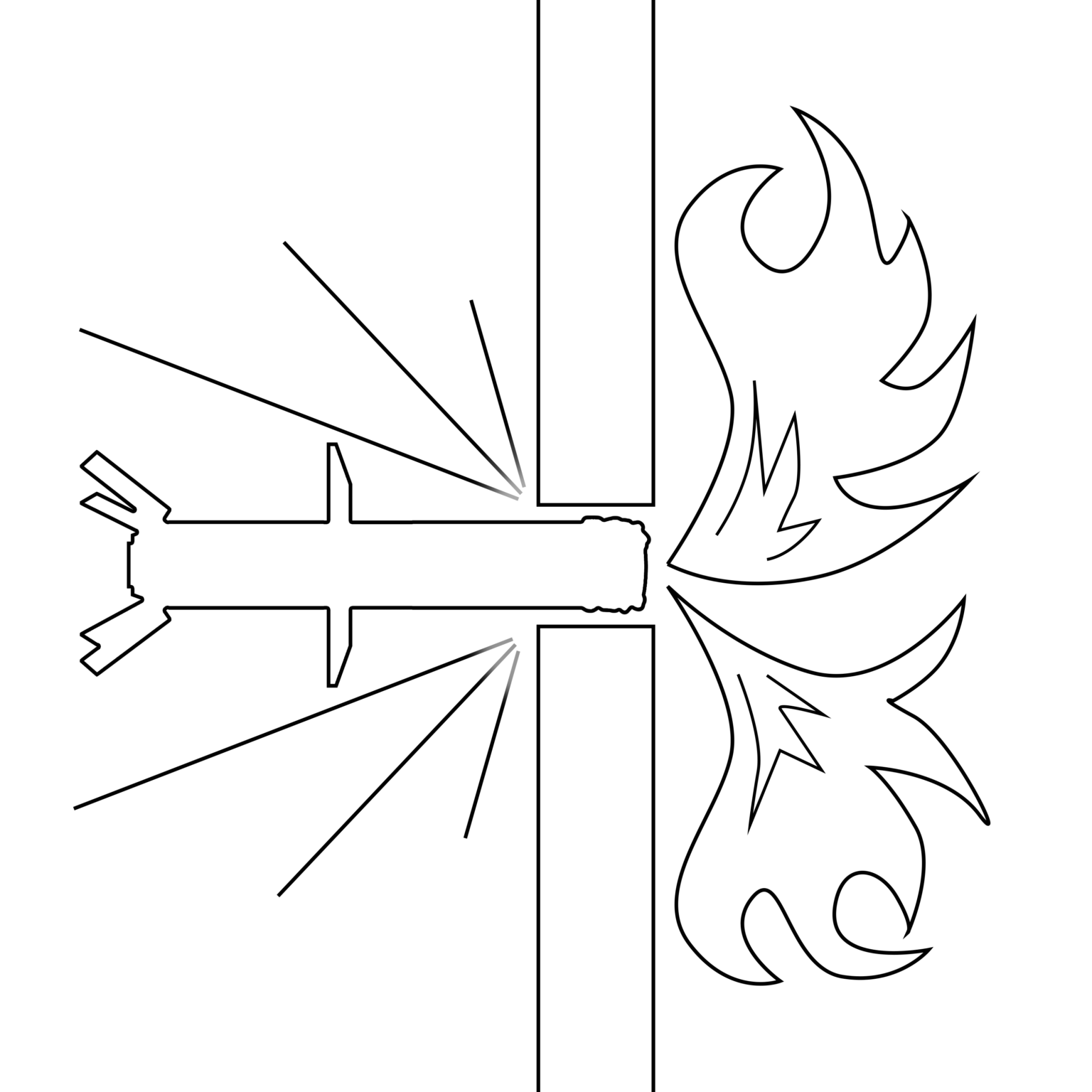 Employ a focused jet of explosive energy to penetrate armour
Employ a focused jet of explosive energy to penetrate armour