82 results
Current Filter
Blast Munition
Use the rapid expansion of gases released by a detonating high explosive compound inside the munition to generate explosive power. Blast munitions are often considered general-purpose munitions and large examples can have powerful and widespread effects on targets such as structures and personnel.

Current Filter
Air-Delivered Bomb
Unpowered munitions dropped from an aerial vehicle, such as a plane or drone. They can be either guided or unguided and range in weight from only a few kilograms to more than 2,000 kilograms — roughly the weight of a car. Heavier air-delivered bombs are among the most destructive munitions in military arsenals.
Read more →
Analyst Note:
This image shows a variety of small air-delivered munitions that have been developed specifically for deployment via UAV. Some of these appear to be original designs, whilst others have been made by modifying existing munitions. This entry reflects those munitions outlined with the red box, but all of the munitions are generally of similar in size and format, and all have tailfin assemblies intended to orient the munition as it falls, just like more traditional air-delivered bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
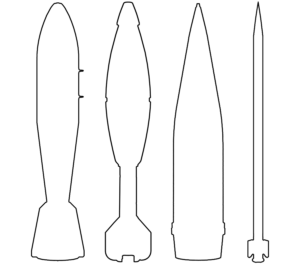
This image shows the nosecone from an Israeli SPICE 250 air-delivered bomb. Whilst generally similar in appearance to the nosecone of the GBU-39, the SPICE 250 nosecone is longer and narrower. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a Mikholit glide bomb, with its warhead removed (green cylinder on the left side of the box). The fins that spring outward when deploye have been taped down. This Mikholit was reportedly recovered by the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) from Hamas, who had captured the bomb after it failed to function when originally deployed by the IDF. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows several remnants of a MAM-L bomb that are typically found after functioning. The actuated fins, as well as the fixed fins, are visible, along with various components of the control section that actuate the fins. The actuated fins attach to the control section, at the rear of the bomb, while the fixed fins attach to the middle of the bomb body. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
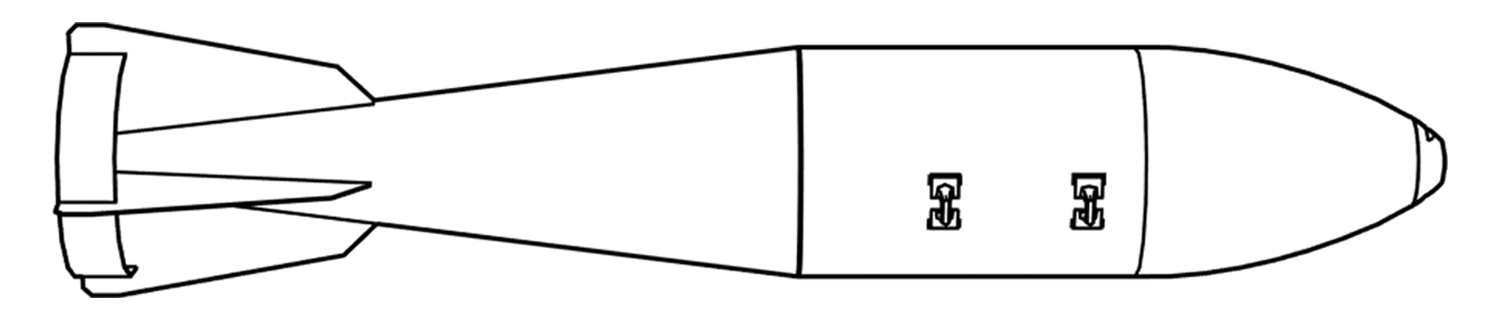
This image shows various munitions remnants, including a fuzewell and two nosecone fragments from GBU-39 Small Diameter Bombs. The presence of two different nosecones indicates that these remnants are from at least two distinct munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows a wing fragment from a SPICE-1000 bomb guidance kit. While there are no remnants of the bomb body visible, it can be determined that a MK 83-series 1,000-pound bomb or similar was used, as MK-83 series bombs are paired with the SPICE-1000 bomb guidance kit to form a complete munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The ZAB-250-200 (ЗАБ-250-200) unguided air-delivered bomb is loaded with 48 kg of a napalm-like thickened incendiary mixture, 8 kg of cotton scraps soaked in kerosene (paraffin), and 4 kg of pyrotechnic composition to aid with ignition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
As with several other images in the OSMP database, the text on this image was added by a social media user prior to its inclusion herein. Rather than a “rocket” as described in the annotation, this image actually shows an air-delivered bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows an aerosurface or ‘strake’ from a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) bomb guidance kit of the type fitted to MK 82-series 500-pound air-delivered bombs. The JDAM kits compatible with MK 82 bombs have aerosurfaces that are affixed near the nose of the bomb—rather than around the widest part of the bomb body, as seen in JDAM kits that are compatible with the larger MK 83 or MK 84 bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
MK 84 unguided air-delivered bombs can be fitted with a variety of tail kits, or with guidance kits which convert them into precision guided munitions (PGMs). When an air-delivered bomb impacts a building or the ground without functioning, the tail or guidance kit may be sheared off. With these separated from the munition—and in the absence of other identifying features, such as a seeker fitted to the nose of the weapon—it becomes very difficult to determine whether the bomb was guided or unguided. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, two GBU-39 guided air-delivered bombs can be seen in their shipping containers, with only the nose and the tail actuation section of the munitions clearly visible. Distinctive packaging such as this can sometimes be used as contextual evidence for the presence of specific munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The arming vane for a nose fuze (painted red) is visible on each of the two leftmost MAB-10B6 air-delivered bombs in this image. As the bomb falls, air passing over the arming vane causes it to spin, arming the fuze. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Labels on munition remnants can provide a host of useful data, including the model designation (in this case, “GBU-39/B”), part number (PN; (“70P998100-1003”), National Stock Number (NSN; “1325-01-526-8728”), serial number (SN; illegible), and Department of Defense Identification Code (DODIC; “EC53”). These codes, and others like them, can often be searched for in databases or provided to technical specialists for further interpretation. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The RAFAEL Advanced Defense Systems SPICE 1000 guidance kit is fitted to MK 83-series 1,000-pound unguided air-delivered bombs to convert them to precision guided munitions. Like the JDAM-ER, it has a deployable wings to provide a ‘gliding’ attack trajectory. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The BLU-117 air-delivered bomb is nearly identical in format to the more common MK 84, but uses the PBXN-109 explosive filler which is more insensitive than the typical explosive compositions found in MK 80-series bombs. The BLU-117 is also coated with a grey, thermally resistant paint, and marked with three yellow bands (as opposed to the green paint with two yellow bands found on standard MK 80-series bombs). These changes were requested by the U.S. Navy for safer storage of these munitions aboard ships. (ARES)
3 Analyst Notes:
This is an image released by the Israeli Defense Forces that shows an F-15I of 69 Squadron Israeli Air Force preparing to take part in a high-profile airstrike on 27 September 2024, in which the leader of Hezbollah, Hassan Nasrallah, was killed.
Analyst Note:
In this image, an F-15C fighter aircraft from 106 Squadron Israeli Air Force is seen carrying two MK 84-series 2,000-pound-class air-delivered bombs fitted with Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) ‘bolt-on’ guidance kits. In U.S. service, this combination is known as the GBU-31. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
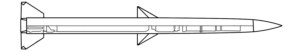
The Joint Direct Attack Munition – Extended Range (JDAM-ER) marries the JDAM guidance kit to a ‘glide bomb’ wing kit developed by the Australian Defence Force, offering a munition with at least three times the range of a standard GBU-38 500-pound-class guided aerial bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, two GBU-39 Small Diameter Bombs are attached to a BRU-61/A bomb rack. The Ukrainian Air Force adapted this American-designed bomb rack to fit their Soviet-designed Mikoyan MiG-29 fighter aircraft. The BRU-61/A can carry up to four GBU-39 air-delivered bombs. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The SPICE family of munitions, manufactured by Israeli aerospace and defence company Rafael, includes two models which use ‘bolt-on’ guidance kits. The SPICE 1000 and SPICE 2000 models convert 1,000- and 2,000-pound unguided aerial bombs, respectively, to precision guided munitions. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
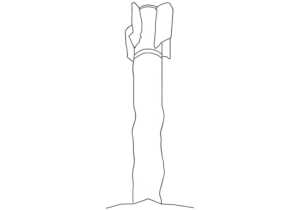
The remnant pictured here is part of a Small Diameter Bomb actuator assembly (‘Tail Actuation Section’), which moves the four tail-fin control surfaces which alter the course of the munition in flight. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The circled remnant is the hardened steel nosecone of the GBU-39, which renders the munition capable of penetrating more than 3 feet (approx. 1 metre) of steel-reinforced concrete. It is one of several components that often survives the detonation of the munition. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image depicts an M117-series unguided aerial bomb. Belonging to a class of weapons referred to as ‘demolition bombs’—which use Tritonal or similar explosive compounds to generate a more powerful blast effect than TNT or Composition B—the M117 is an American design which dates to the Korean War era and is rarely seen in service with modern armed forces. (ARES)
2 Analyst Notes:
This munition is assessed to be one of the Small Diameter Bomb (SDB) I variants (GBU-39 series), rather than one of the SDB II 'StormBreaker' (GBU-53 series) munitions, on the basis of contextual information. 'Small Diameter Bomb' is the manufacturer's terminology, whilst 'GBU-39' is the U.S. Air Force designation (also used by many other operators). (ARES)