Analyst Note:
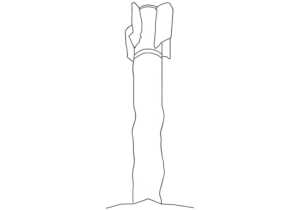
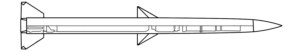
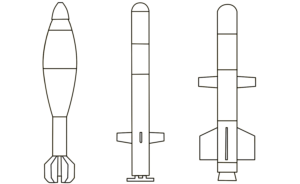
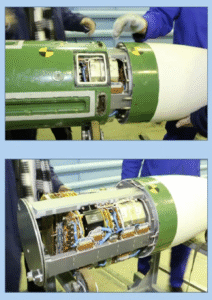
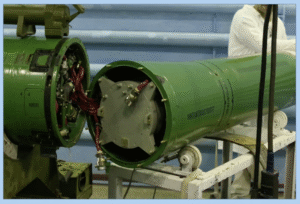
The munition indicated is a one-way-attack (OWA) UAV fitted with a PG-7-series high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead. Not enough of the warhead is visible to provide a positive ID on which model of PG-7-series projectile it was harvested from. (ARES)