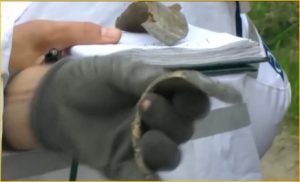
Analyst Note:
The physical features of this munition indicate that it is most likely an Iranian 60 mm ‘high explosive, long-range’ (“H.E. L.R.”) mortar projectile fitted with an AZ111A2 impact fuze. However, positive identification cannot be made based on the source imagery. (ARES)
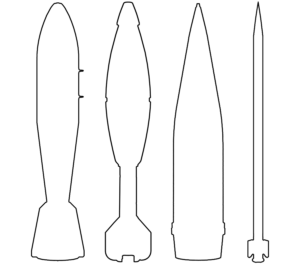
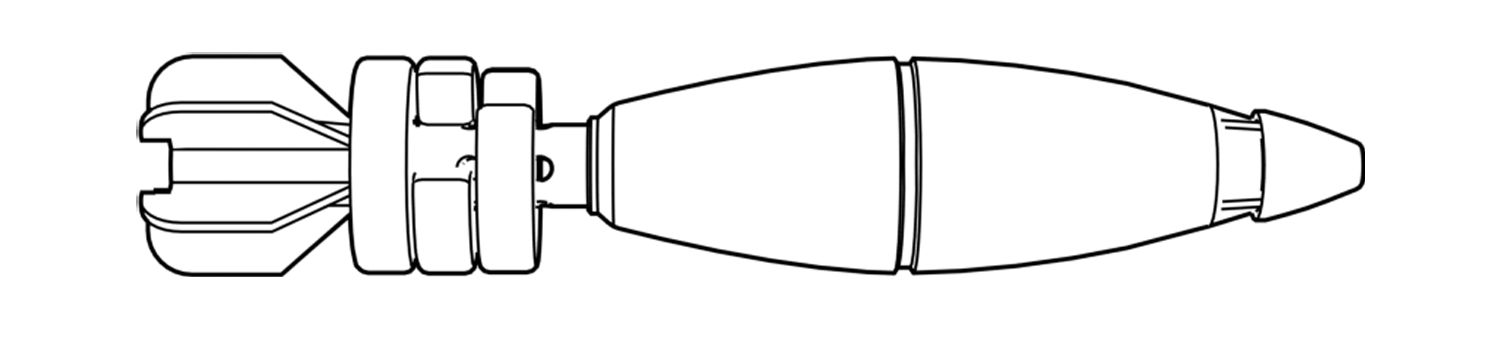 Relatively small projectiles with a distinctive ‘teardrop’ shape
Relatively small projectiles with a distinctive ‘teardrop’ shape