46 results
Analyst Note:
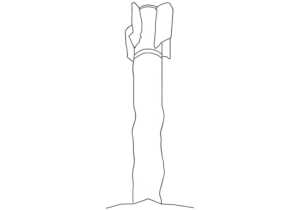
This image shows a close up view of an actuator assembly from an AGM-114 ‘Hellfire’ series missile. This assembly is what actuates the control fins, and the attachment point for one of the control fins is visible at the bottom right of the image. This assembly belongs to the control section, which is the rearmost section of the missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
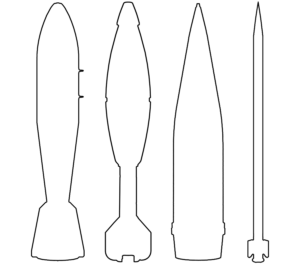
This image shows remnants of two different rocket motors from AGM-114 series Hellfire missiles. While it cannot be determined by these entries alone, images of the damage from the strike associated with this image, gathered by Mwatana, indicate that both of these AGM-114 missiles were the kinetic AGM-114R9X variant. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the rocket motor of an AGM-114 "Hellfire" series guided missile found in Jordan during the 12 day conflict between Israel and Iran. This specific Hellfire missile is likely an air-to-air "C-UAS" variant used to intercept one-way attack drones, such as those launched by Iran towards Israel, rather than the more common air-to-surface Hellfire missile variants. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This image shows the pneumatic accumulator, or ‘accumulator bottle’, of the AGM-114R9X missile. The accumulator bottle stores gas that is used to actuate the fins, adjusting the trajectory of the missile in flight. All AGM-114 Hellfire-series missiles have an accumulator bottle. The accumulator bottle is a fragment that often survives intact, even in Hellfire missile variants that carry an explosive payload. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Contextual images of the damage caused by this munition indicate the remnant pictured is from the AGM-114R9X variant of the Hellfire missile, a kinetic munition which does not carry an explosive warhead. This remnant cannot be differentiated from either other AGM-114 or the AGM-179 JAGM variants based off this image alone. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This F-16I fighter aircraft from the Israeli Air Force is carrying a CATM-120 inert missile simulant (indicated). These devices are used for training purposes, being designed to replicate the weight and centre of gravity of a live munition. They lack any means of propulsion and are not released from the aircraft. The CATM-120 can be differentiated from the AIM-120 missile series by the presence of only blue bands on the missile, denoting both an inert rocket motor and an inert payload. A ‘live’ AIM-120 will have two brown bands on the rear section of the missile (the rocket motor), and a yellow band on the forward, or warhead, section. An AIM-120 with an inert warhead, but a live rocket motor, will have a blue band on the warhead and two brown bands on the rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
This F-16I fighter aircraft from 107 Squadron Israeli Air Force is carrying a CATM-120 inert missile simulant (indicated). These devices are used for training purposes, being designed to replicate the weight and centre of gravity of a live munition. They lack any means of propulsion and are not released from the aircraft. The CATM-120 can be differentiated from the AIM-120 missile series by the presence of only blue bands on the missile, denoting both an inert rocket motor and an inert payload. A ‘live’ AIM-120 will have two brown bands on the rear section of the missile (the rocket motor), and a yellow band on the forward, or warhead, section. An AIM-120 with an inert warhead, but a live rocket motor, will have a blue band on the warhead and two brown bands on the rocket motor. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The AGM-179 Joint Air-to-Ground Missile (JAGM) is derived from the AGM-114 Hellfire series of air-to-surface missiles—and thus shares physical characteristics in terms of general construction, including rear fin placement. The marked weight of 52.0 kg (115 lbs) is generally believed to be an indicator that the rocket motor is from a JAGM; however, remnants marked with this weight have been observed from several years before the JAGM was initially fielded. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
In this image, four AGM-114 Hellfire-series missiles can be seen fitted to an M299-series missile launcher, itself attached to the stub wings of this Israeli AH-64 Apache helicopter. In theory, the Apache could be armed with up to sixteen Hellfire missiles, but fewer are carried in practice to allow for other weapons and sensor payloads (ARES).
Analyst Note:
This image shows a component believed to be part of the folding-blade assembly used in the AGM-114R-9X variant of the Hellfire missile. Blades are used in place of an explosive payload to create a kinetic weapon that achieves a practical level of lethality whilst minimising collateral harm. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
Little is known with certainty about the AGM-114-R9X variant of the Hellfire missile, although it has been associated with high-profile targeted killings including those of senior al-Qaeda figures. The weapon functions as a kinetic-impact munition, using pop-out blades—rather than an explosive warhead—to reduce the prospects of collateral harm. (ARES)