Analyst Note:
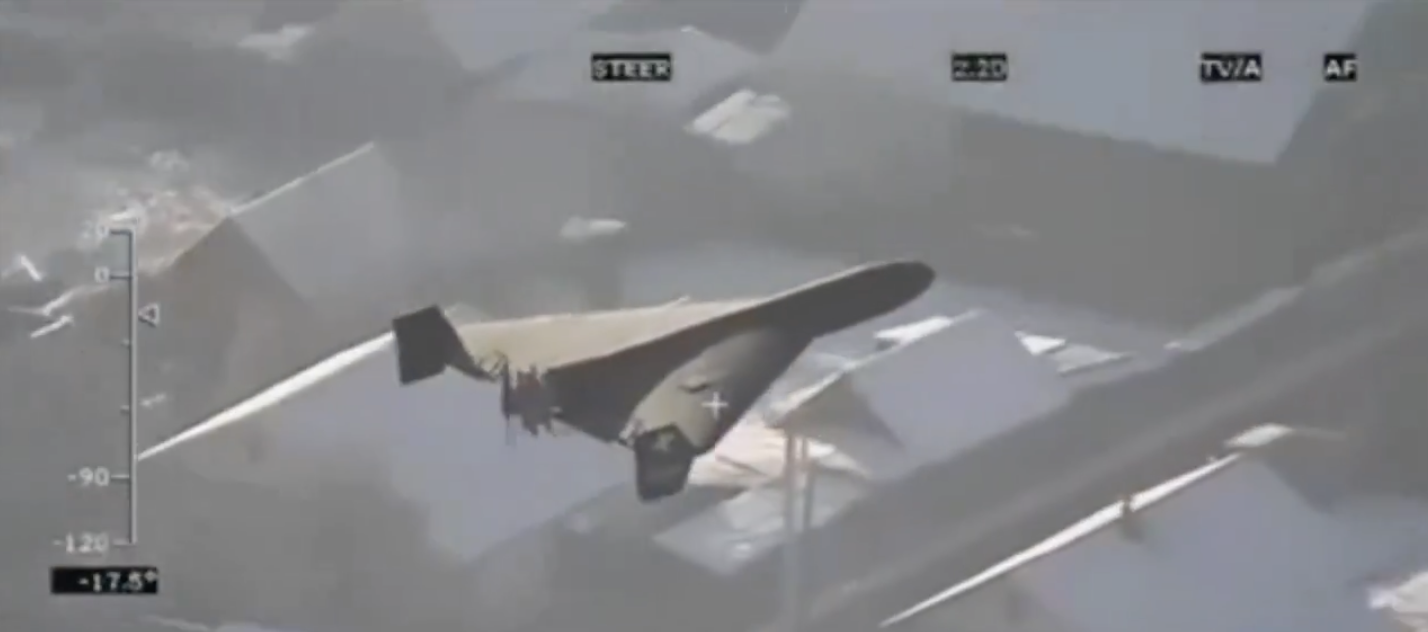
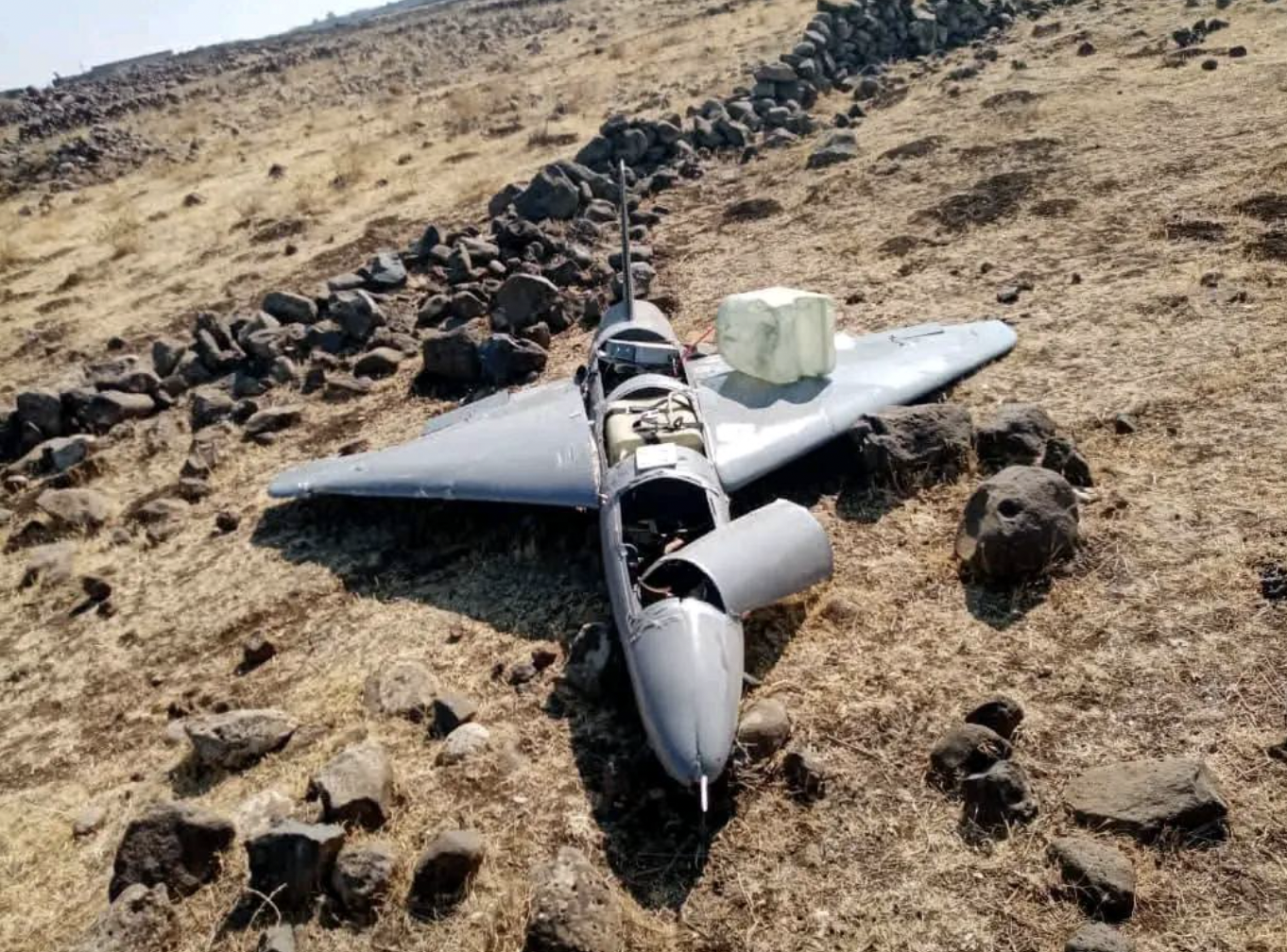
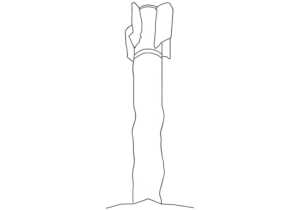
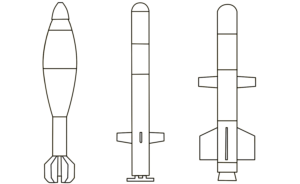
This image shows the rear portions of two different two different Spike Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) missiles, which each include the control section and part of the rocket motor.
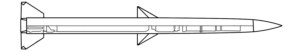
The Spike NLOS has been in service with Israel since 1987, and is currently in its sixth generation, or iteration, which comprises an unknown number of variants. At least three different warhead configurations are reported: high explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG), high explosive anti-tank (HEAT), and a ‘multipurpose’ or anti-structure variant with a penetrating blast and fragmentation warhead. (ARES)