13 results
Current Filter
Tamir
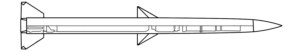
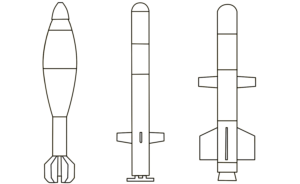
An Israeli-designed surface-to-air missile which became operational in 2011 as part of the Iron Dome air defence system. The Tamir interceptor has an effective range of 70 km and can intercept short-range rockets, artillery projectiles, mortars, and UAVs (drones),as well as providing a more limited capability against aircraft and cruise missiles. A ground-based radar is used to provide midcourse guidance updates to the missile, and an onboard proximity fuse detonates the warhead once near the target. These interceptor missiles are primarily used against munitions projected to land in populated areas such as urban centres and military bases. The system has seen frequent use by Israel and has also been sold to the United States in limited quantities.
Analyst Note:
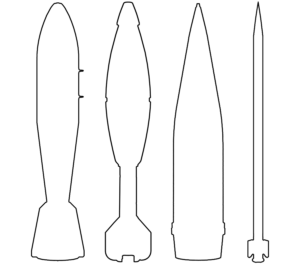
This image shows most of the forward half of a Tamir surface-to-air missile, including the guidance section and warhead, as fired by launchers in the Iron Dome system. These interceptor missiles are fast and manoeuvrable with a relatively small explosive payload. Their construction and low yield means that remnants are often recovered largely intact. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
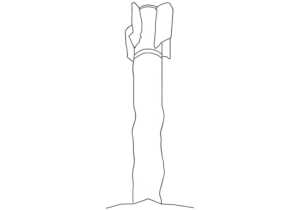
This image shows the nosecone from an Israeli Tamir surface-to-air missile. This component is often found as a remnant after the functioning of the missile. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The Tamir Interceptor is the missile fired from Israel’s Iron Dome defence system to intercept incoming rockets, missiles, projectiles, and unmanned aerial vehicles (‘drones’). The Tamir uses a warhead with a relatively small explosive yield, which typically results in the guidance section, nosecone, and (spent) rocket motor falling to the ground relatively intact after functioning. (ARES)

Collection
Israel and Gaza 2023 – 2025
On 7 October 2023, Hamas militants breached the heavily-fortified border separating Israel and the Gaza Strip, attacking numerous towns and villages. More than 1,000 people in Israel were reported killed, with more than 250 taken hostage and moved to Gaza. In response, Israel has launched one of its largest military operations of recent decades, seeking […]