9 results
Analyst Note:
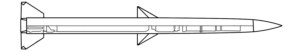
This image shows the top of the booster of an Arrow 3 interceptor missile, where it connects to the kill vehicle. The Arrow 3 was jointly developed by the United States and Israel, and first entered service in 2017. The date of manufacture marking (“DATE OF MFG: 05/2018”) indicates that this booster was produced in the year after the Arrow 3 first entered service. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
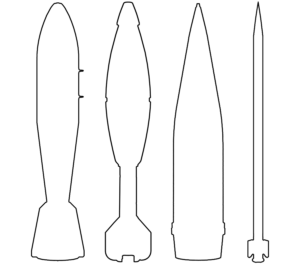
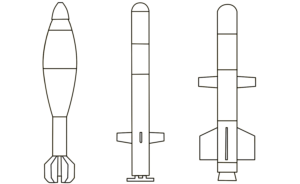
This image shows the booster of an Israeli Arrow 3 interceptor missile. The Arrow 3 is designed to engage ballistic missiles and is capable of exo-atmospheric interceptions. Once the booster is expended, it separates from the ‘kill vehicle’. The kill vehicle has a sustainer motor that propels it towards the incoming ballistic missile, and uses kinetic impact, rather than an explosive warhead, to disable or destroy its target. This is sometimes called the ‘hit-to-kill’ principle. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
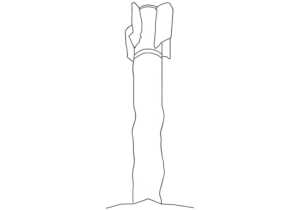
Although this munition started out life as a mortar projectile of the M492-pattern, it has been modified to be dropped from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and, in its present state, could not be fired from a conventional mortar. As such, it is correctly classified here as an air-delivered bomb. (ARES)
Analyst Note:
The fin assembly in the image bears a strong resemblance to those of other munitions employed in the same incident that have been identified as M49A2 mortar projectiles modified to be delivered by UAV. (ARES)