OSMP Collection
What Are Bomb Guidance Kits?
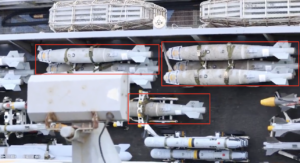
Bomb guidance kits are fitted to unguided (‘dumb’) bombs to convert them into precision guided munitions (PGMs). Sometimes referred to as ‘bolt-on’ guidance kits if they are relatively simple to install, bomb guidance kits can provide a variety of capabilities that vary according to cost and what the user needs.
Most guidance kits replace the fixed fins of an unguided air-delivered bomb with actuated fins that can ‘steer’ the munition as it falls. Some kits will also include additional or alternative guidance or control components in the nose of the munition. These additional components frequently survive detonation of the bomb, and can be diagnostic in identifying the family or model of munition used.

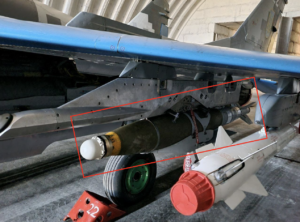
This entry in the OSMP shows a MK 84 unguided air-delivered bomb fitted with a JDAM guidance kit, but how can you distinguish the munition from the guidance kit? The illustration on the right explains (source: IDF Farsi).
The way guidance is achieved varies by kit, but Global Position System (GPS) data, inertial navigation system (INS) data, laser guidance, and electro-optical (EO) guidance are common.
Some common kits are the U.S. Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) kits, which use GPS/INS guidance, and the Israeli SPICE 1000 and SPICE 2000 kits, which use EO and GPS/INS guidance. The U.S. Paveway and Israeli LIZARD series use laser guidance.
When munitions are combined with a guidance kit, they are sometimes given a new designation by manufacturers or in military service, such as the U.S. ‘Guided Bomb Unit’ (GBU) designation. For example, when a 2,000-pound MK 84-series air-delivered bombs is fitted with a JDAM kit, it is referred to as a GBU-31. Combinations may have further variant designations, such as GBU-31(V)1, etc.