Analyst Note:
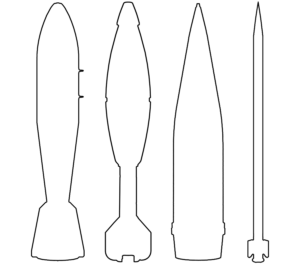
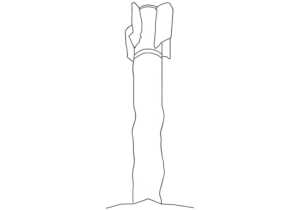
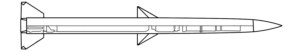
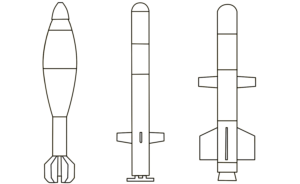
This image shows a North Korean 170 mm artillery projectile, as fired by the M-1978 Koksan self-propelled artillery gun. Very little is known of the M-1978 Koksan due to the secretive nature of North Korean arms development, but both high explosive and rocket-assisted high explosive projectiles are believed to be available. The designations ‘M-1978’ and ‘Koksan’ were applied by American military analysts identified the system in Koksan, North Korea, in 1978. (ARES)